
[ad_1]
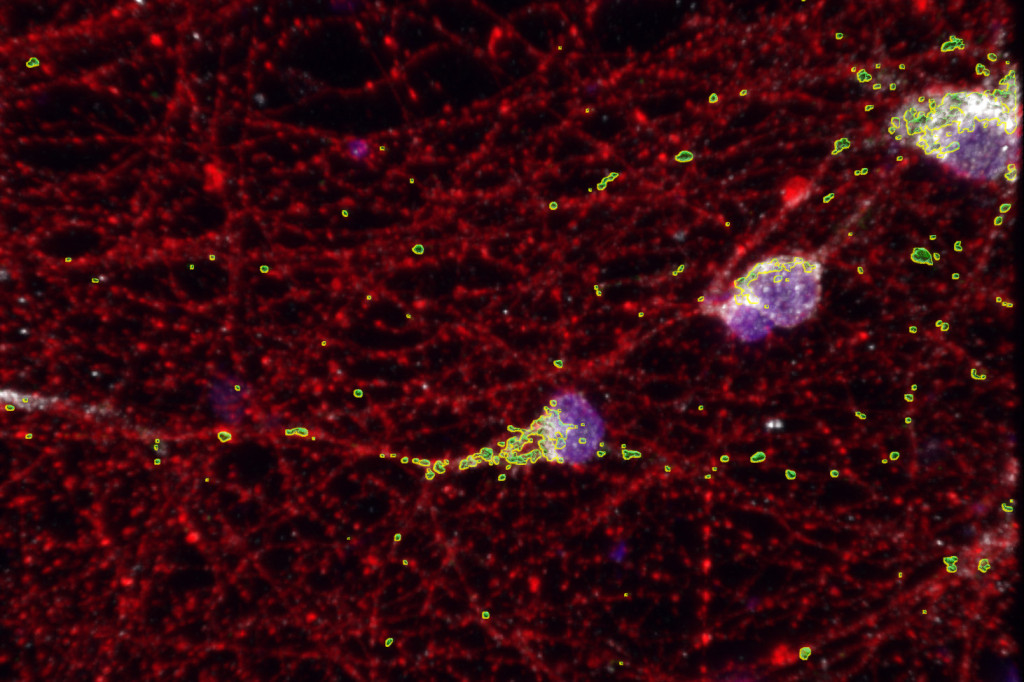
The energy-making organelles known as mitochondria (proven in inexperienced) that work inside cells to make vitality aren’t working as they need to within the neurons (proven in pink) of individuals with fragile X syndrome. UW–Madison researchers have recognized a protein and gene concerned on this mitochondrial dysfunction, in addition to a possible therapy. Picture by: Minjie Shen
Fragile X syndrome, the most typical type of inherited mental incapacity, could also be unfolding in mind cells even earlier than delivery, regardless of usually going undiagnosed till age 3 or later.
A brand new research printed at present within the journal Neuron by researchers on the College of Wisconsin–Madison confirmed that FMRP, a protein poor in people with fragile X syndrome, has a job within the operate of mitochondria, a part of a cell that produces vitality, throughout prenatal growth. Their outcomes basically change how scientists perceive the developmental origins of fragile X syndrome and recommend a possible therapy for mind cells broken by the dysfunction.

Xinyu Zhao is a neuroscience professor and neurodevelopmental ailments researcher at UW–Madison’s Waisman Heart. 4 postdoctoral fellows in her lab led the research.
The research, led by 4 postdoctoral fellows — Minjie Shen, Carissa Sirois, Yu (Kristy) Guo and Meng Li — working within the lab of the lab of Xinyu Zhao, neuroscience professor and neurodevelopmental ailments researcher at UW–Madison’s Waisman Heart, discovered FMRP regulating a gene known as RACK1 to advertise mitochondrial operate. Utilizing a drug to reinforce mitochondrial operate, they have been capable of rescue mind cells broken by lack of FMRP.
People with FXS could current developmental delays — not sitting, strolling or speaking at anticipated ages — in addition to delicate to extreme mental incapacity, studying disabilities and social and behavioral issues. About half are additionally identified with autism spectrum dysfunction.
In earlier analysis, Zhao discovered that mitochondria in mice with an FMRP deficiency that imitates FXS have been smaller and unhealthy. Diving deeper, in addition they found that FMRP regulates genes concerned in mitochondria fission-fusion, a course of through which mitochondria fuse into a much bigger form with the intention to produce extra vitality for the cell.
For the research, researchers grew mind cells known as neurons grown from induced pluripotent stem cells. As a result of the stem cells got here from individuals with FXS, the researchers might research the event of the dysfunction at a mobile degree, figuring out whether or not mitochondria in human cells skilled points much like these in mice.
“And certainly, we discovered that human neurons even have fragmented (smaller) mitochondria,” Zhao says. Additionally they discovered fewer mitochondria in neurons derived from FXS sufferers, which they didn’t see within the neurons of the mice modeling FXS.
“In human neurons, it’s a deficit in twofold. Not simply fission-fusion, but in addition possible within the manufacturing of mitochondria,” Zhao says.
Though it has lengthy been recognized that FMRP is deeply concerned in FXS, the brand new discovery pinpoints a job for the protein in early growth of the situation.
Signs of FXS current lengthy after the child is born. Many infants seem like growing usually earlier than exhibiting slower growth, autistic options or developmental deficits. Youngsters with FXS are usually identified at three years of age or older.
“Which implies many scientists have been considering that FMRP is extra essential for the postnatal maturation state,” Zhao says.
FMRP is protein that regulates using messenger RNA, kind of a working copy of DNA used to provide the proteins that make issues occur in cells. The researchers discovered that most of the mRNA strands that work together with FMRP are implicated in autism, offering a molecular hyperlink between FXS and autism spectrum dysfunction. Unexpectedly, many FMRP-bound mRNAs are expressed by genes categorised as important — genes which might be very busy throughout prenatal growth however much less lively after delivery.
“Which means that FMRP has a operate in prenatal growth that we now have not likely considered earlier than,” Zhao says. “The truth that we discovered that FMRP additionally regulates prenatal growth is admittedly attention-grabbing and is definitely indicating that what we see in fragile X syndrome, a few of the results already occurred inside the prenatal growth.”
A kind of important genes is RACK1, recognized for the primary time as taking part in a job in FXS.
“When RACK1 is decrease in fragile X neurons, the mitochondria are struggling and the neurons exhibit mitochondrial deficit and hyperexcitability, like immature neurons. However after we reintroduce RACK1, we will rescue this,” Zhao says.
Utilizing cultured neurons derived from people with FXS to display for medicine, the researchers discovered a drug known as leflunomide that corrected mitochondrial deficits. The therapy improved mitochondrial operate and lowered the neurons’ hyperexcitability.
Subsequent, Zhao needs to do an in depth biochemical evaluation of mitochondrial dysfunction and work out which key proteins are much less current in FXS-affected neurons. She can be engaged on higher understanding how RACK1 and leflunomide work to rescue mitochondrial operate.
Different collaborators on the research embrace Waisman Heart investigators Qiang Chang, Anita Bhattacharyya, Andre Sousa, Daifeng Wang, Donna Werling and UW–Madison neuroscience professor Jon Levine.
This analysis was supported by grants from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R01MH118827, R01NS105200, R01MH116582, R01MH118827, R01HD064743, R01NS064025, R01AG067025, U01MH116492, P51 OD011106, U54HD090256, P50HD105353, R24HD000836 and T32 GM141013) and the Division of Protection (W81XWH-22-1-0621), in addition to funding from the Mind Analysis Basis, Wisconsin Alumni Analysis Basis, Mind and Habits Analysis Basis, Simons Basis, FRAXA Analysis Basis, Autism Science Basis and UW–Madison awards together with the Jenni and Kyle Professorship, Vilas College Mid-Profession Investigator Award, Kellett Mid-Profession Award, SciMed scholarships, Stem Cell and Regenerative Medication Heart postdoctoral fellowship and Hilldale Undergraduate Analysis Fellowship.
[ad_2]