
[ad_1]

College students look at graphs exhibiting how enzymes and substrates work together. Enzymes are organic catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by decreasing the activation power required for the response to happen. Most often, the speed of an enzyme-catalyzed response will increase with a rise in substrate focus.
The graphic exhibits a conventional lock-and-key mannequin of enzyme and substrate interactions. The form of the enzyme matches to the form of the substrate, which initiates the response. This mannequin explains the specificity of enzyme-substrate interactions. For instance, the lactase enzyme is particular to the lactose protein.
Initially, when the substrate focus is low, the enzyme’s energetic websites usually are not absolutely occupied. As extra substrate molecules can be found, they’ll simply bind to the energetic websites, resulting in a rise within the charge of the response.
Because the substrate focus will increase, the speed of the response additionally will increase. At a sure level, the enzyme’s energetic websites develop into practically saturated with substrate molecules. At this stage, the enzyme is performing at its most capability. Different elements can have an effect on the speed of response, equivalent to temperature and pH.
Enzymes and Substrates Worksheet
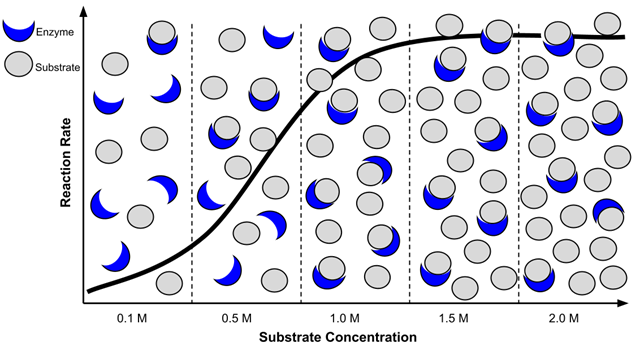
College students look at a graphic that illustrates how enzymes and substrates work together. They rely the variety of accessible molecules at every focus. Evaluation reveals that the response charge is quick at first, however ranges off when the substrate is saturated.
Within the second part, college students additionally have a look at the variety of merchandise created over time. As soon as the enzyme has run out of substrates to work together with, the response stops.
College students may find out about these processes on this enzyme coloring exercise. I typically cowl the fundamentals of enzymes in each freshman biology and AP Biology. AP Biology does further investigations with enzymes, equivalent to exploring yeast and catalase reactions.
[ad_2]