
[ad_1]
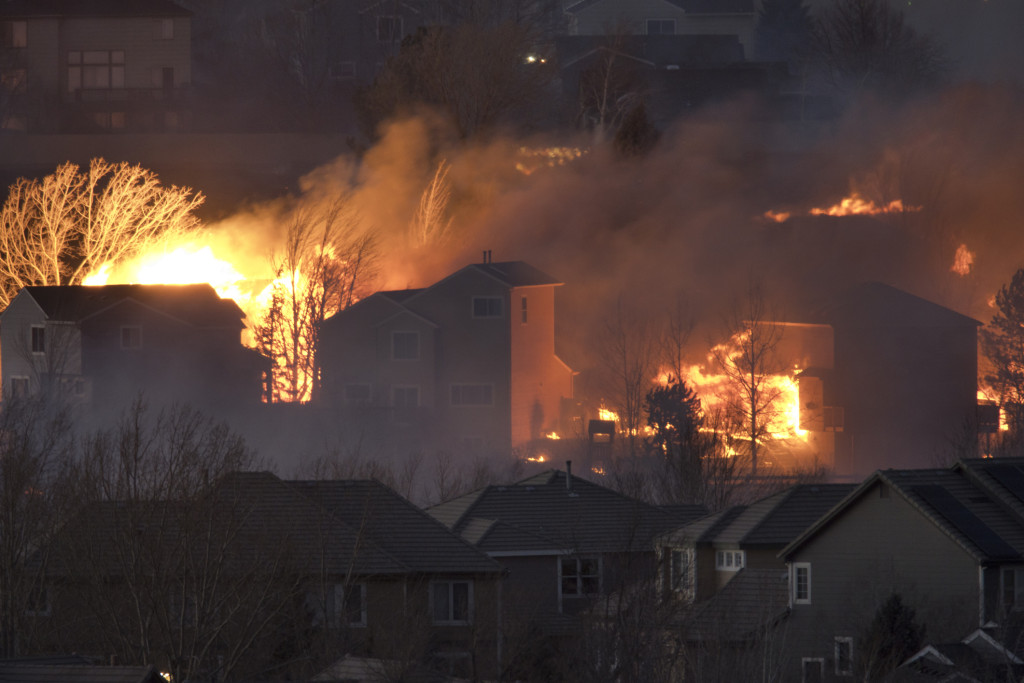

Excessive winds fueled wildfires that tore throughout open grasslands and thru houses in Superior, Colorado, in 2021. Over 500 houses had been destroyed. Photograph by iStock
When individuals consider wildfires, they usually consider big forests burning and flames leaping from tree to tree. However based on new analysis led by Volker Radeloff, a professor of forest and wildlife ecology at College of Wisconsin–Madison, in america, the biggest areas close to people burned by wildfires are grass and shrublands, not forests.
The examine was revealed within the journal Science just lately.
Radeloff has studied the areas the place individuals and wildlands meet for years. Often called the Wildland City Interface, or WUI, these areas cowl about 10% of land in america however are house to about one-third of the inhabitants. The WUI (pronounced “woo-ee”) was initially a instrument utilized by the U.S. Forest Service to help with wildfire administration within the western U.S.
The WUI can include a variety of wildland vegetation equivalent to timber, shrubs, grasses, wetland vegetation, mangroves, moss and lichen. Every kind of vegetation requires totally different administration methods, as they regenerate after fireplace in another way and are affected by environmental elements like precipitation in distinctive methods.
As Radeloff explains, many individuals take pleasure in residing in these locations as a result of they wish to be close to the facilities of nature. However these areas are additionally scorching spots for environmental conflicts like wildfires, the unfold of ailments from animals, habitat fragmentation and lack of biodiversity.
In areas with rising populations, such because the American sunbelt, extra human improvement is increasing the WUI. Add to {that a} altering local weather with hotter, drier circumstances, and the chance rises that wildfires will have an effect on people extra incessantly.
“Texas is now the state with the biggest enhance within the variety of WUI homes. California had that distinction for a very long time,” Radeloff says.
Whereas the entire space burned by grass and shrubland fires is far bigger than forest fires, grass and shrublands are additionally rather more widespread than forests. They burn and transfer quicker than forests, which means grassland fires can unfold to a bigger variety of houses than a forest fireplace may.
Utilizing information from the U.S. Census Bureau and NASA, and with assist from the U.S. Forest Service, Radeloff and his crew constructed information units that present the place wildfires burned houses and point out if these houses had been rebuilt.
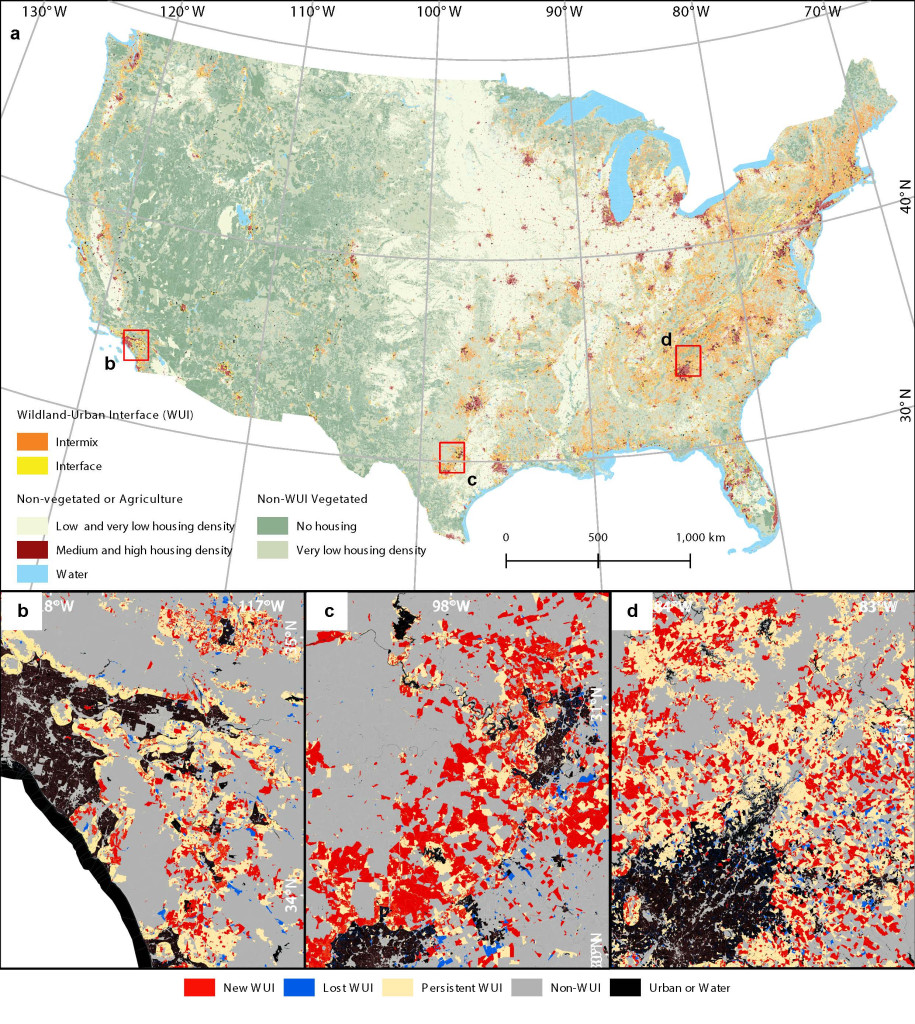
The wildland-urban interface (WUI) in 2020 throughout the conterminous US, and adjustments in WUI space from 1990 to 2020 close to Los Angeles (a), San Antonio (b), and Atlanta (c). Picture courtesy of Volker Radeloff
The researchers discovered that the danger of wildfire in any form of WUI vegetation shouldn’t be deterring the event and rebuilding of houses in areas which have burned previously.
That’s particularly regarding for houses in grassland and shrubland as a result of the vegetation, which might grow to be gas for fireplace, recovers rather more shortly than a forest would. Meaning there’s extra gas for a hearth to burn once more in the identical grass and shrubland space extra incessantly.
The difficulty shouldn’t be a scarcity of house owner information, Radeloff explains. Individuals who select to reside in these areas usually know the danger of fireside exists, he says, but it surely’s a danger they’re keen to take. Whether or not they really feel a connection to the land, a need to reside close to a good looking vista or select to rebuild in a location that already has electrical energy and plumbing working to it, individuals nonetheless select to reside in areas susceptible to burning.
“It’s often a lot simpler to remain in the identical place to construct a home,” Radeloff says. “Getting homes rebuilt, companies reestablished shortly, is vital. So, to only pack up and go is basically laborious for a group to do and occurs fairly hardly ever.”
There are methods owners can harden their houses in opposition to fireplace, although, and Radeloff believes studying from the houses that don’t burn could be a step in the best path for those who select to rebuild after a hearth.
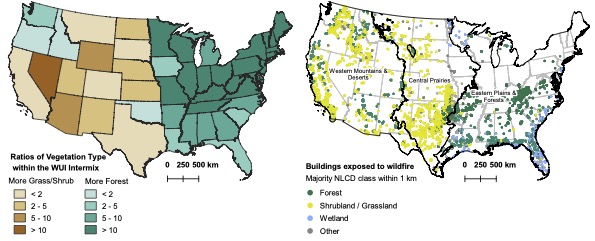
The map on the left compares grassland to forest land in states throughout the US. On the best, is a map that signifies buildings uncovered to wildfire organized by the form of WUI vegetation throughout america. Picture courtesy of Volker Radeloff
Nevertheless, Radeloff says this burden shouldn’t be solely on the house owner. He believes there may be room for policymakers to affect how ready a group is and the place zoning ought to permit new housing developments.
“As a rustic, we’ve realized to not construct extensively in floodplains. We should always do one thing comparable for wildfires as effectively,” he says.
Serving to varied policymakers in any respect ranges of presidency perceive the distinction between how grasslands and forests burn in another way, or that totally different vegetation sorts all require totally different administration approaches, may assist inform higher coverage.
Guaranteeing {that a} group in danger has a longtime evacuation plan and a transparent notification system for evacuation is one other space for enchancment Radeloff sees, particularly in locations the place these wildfires usually tend to enhance. He says that a greater notification system and evacuation plans may have helped cut back the toll of the latest fires that burned the city of Lahaina in Hawaii.
“That doesn’t cease the lack of houses, but it surely stops the lack of life,” he says.
Because the world continues to heat, understanding the increasing areas the place people and wildlands meet will probably be more and more vital. Utilizing information units like these Radeloff and his crew produced can assist owners and policymakers know what dangers could also be coming and the place how they will higher put together for them.
[ad_2]