
[ad_1]
Each fuel and liquid chromatography serve the identical goal, i.e., separating the parts of any combination. However they differ tremendously if we discuss their working mechanisms, parts used and the required situations.
Gasoline chromatography makes use of fuel as its cellular section for transferring the particles of the pattern contained in the column. In distinction, in liquid chromatography, the cellular section used to maneuver pattern particles is liquid in nature.
The precept behind fuel chromatography is that it makes use of, separates and analyses the compounds of their unstable or gaseous state. In distinction, the liquid chromatography approach separates the dissolved ions, particles or molecules in a liquid.
The fuel chromatography works beneath a really excessive temperature to maintain the pattern in its unstable state. Compared, liquid chromatography works beneath high-pressure situations that may push and separate the constituent particles of a pattern.
In analytical chemistry, individuals typically get confused between these two necessary chromatographic strategies. Thus, right here we goal to offer you all the key variations between fuel and liquid chromatography.
Content material: Gasoline Vs Liquid Chromatography
- Comparability Chart
- What’s Gasoline Chromatography?
- What’s Liquid Chromatography?
- Key Variations
- Conclusion
Comparability Chart
| Foundation of Traits | Gasoline Chromatography |
Liquid Chromatography |
|---|---|---|
| That means | It’s the chromatographic approach that aids the separation and evaluation of unstable compounds in a gaseous section. | It’s the chromatographic approach which separates ions or molecules current within the dissolved state in a solvent. |
| Additionally Generally known as | Gasoline-liquid chromatography or vapour-based chromatography | Liquid-solid chromatography |
| Cellular section | Gasoline Instance: Helium |
Liquid Instance: Silica |
| Stationary section | Liquid molecules current within the strong help | Stable adsorbent |
| Pattern | Unstable | Comparatively much less unstable |
| Chromatographic Mattress Form | Column | Column or airplane |
| Detectors | The standard of resolutions relies on the volatility of the parts current within the combination | Right here the detectors are: • Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopic detector • Refractive Index detector (RID) • LC/MS |
| Column | Skinny, lengthy and slender capillaries or packed columns | Quick and wide-sized packed columns |
| Dependency of Decision | The standard of resolutions relies on the volatility of the parts current within the combination | Right here, the decision depends on the composition of the combination and the polarity of the molecules current. |
| Operative Situations | Takes place in excessive temperatures | Works beneath excessive strain |
| Temperature Management | Required | Not-required |
| Use | Within the separation of the unstable compounds | Within the separation of the soluble constituent molecules |
| Expense | Low-cost | Excessive-cost |
| Time consumption | Takes comparatively much less time | Very time -a consuming course of |
| Software | • Separation of oils and fatty acids • Separating the plant’s pigment • Drug abuse testing • Isolating the unstable pesticides from the pattern • Testing the toxins and different dangerous chemical substances within the air |
• Separation of inorganic ions from the pattern • Separation of sugars, polymers, nucleotides, nutritional vitamins, peptides, proteins, lipid molecules and so forth. |
What’s Gasoline Chromatography?
Gasoline chromatography is a really famend approach in analytical chemistry used to separate and analyse the constituents of the compounds of their unstable state.
Gasoline chromatography makes use of fuel as a cellular section to hold the pattern molecules over the stationary section. This gaseous section carries the pattern molecules on the stationary section contained in the column.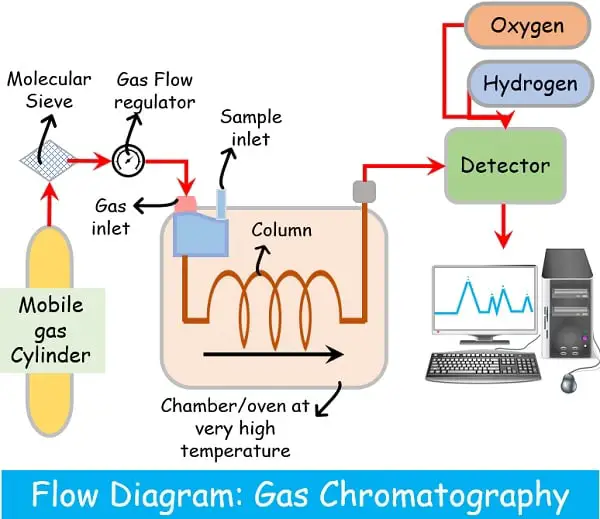
Separation of Parts
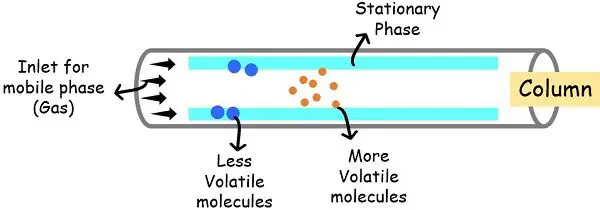
The separation of the parts in fuel chromatography depends on the partition equilibrium of the parts between the cellular and stationary section.
The extent of separation relies upon upon the boiling level of the parts. The upper the boiling level, the extra slowly the element strikes by way of the stationary section.
The molecules with a low boiling level work together much less with the stationary section and extra with the cellular section, transferring quicker by way of the column.
Whereas these with larger boiling factors work together much less with the cellular section and extra with the stationary section, transferring slowly inside the column.
Parts of Gasoline Chromatography
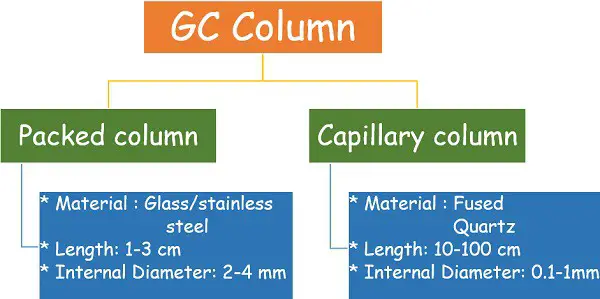
Column
It’s a long-tube-like coil that is still compactly organized in a chamber. The column comprises an adsorbent materials that acts because the stationary section for the chromatography.
 There are two kinds of columns:
There are two kinds of columns:
- Packed column
- Capillary column
Pattern
The pattern ought to be unstable if you wish to analyse it with fuel chromatography. It may be both in gaseous or liquid kind.
Whether it is within the liquid state, the pattern must get transformed into its vaporised kind.
The pattern used ought to have the ability to tolerate larger temperatures. Additionally, we must always be mindful the unique nature and exercise of the pattern don’t change throughout volatilisation.
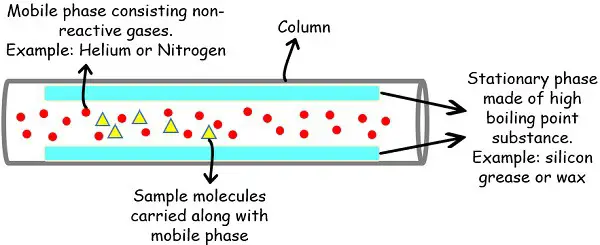
Stationary Section
The stationary section supplies the platform on which the molecules run. The internal partitions of the column have the liner of adsorbent materials that acts as a stationary section.
Each liquids, in addition to strong supplies, can serve the function of the stationary section. Furthermore, the fabric used should have the ability to bear very excessive temperatures within the chamber or oven.
If the stationary section is strong, we discuss with this system as gas-solid chromatography. Whereas, when the stationary section is liquid, we discuss with this system as gas-liquid chromatography.
Cellular Section
The fuel used for the cellular section is mostly inert or unreactive by nature. This avoids any chemical exercise between pattern and fuel or fuel and stationary section.
Principally the analytical laboratories choose helium or nitrogen fuel for this goal because the former is inert whereas the latter is unreactive.
Molecular sieve
This stay hooked up between the fuel cylinder and the chamber. It filters out all of the undesirable contaminations like hydrocarbons, oxygen or water content material that would hamper the method.
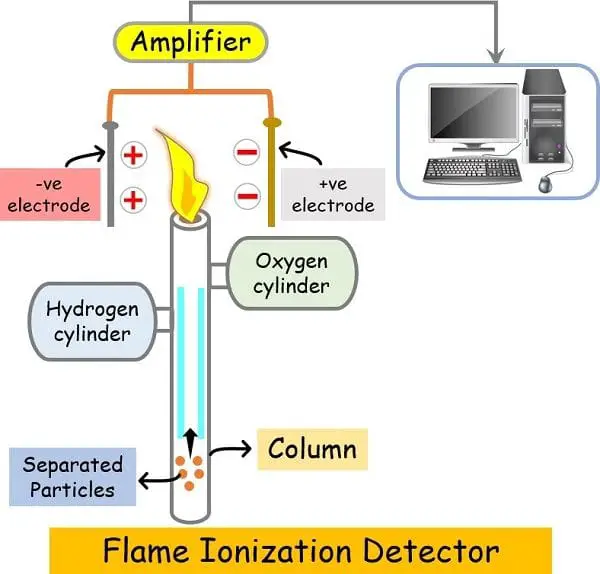
Detector
A detector detects the elute molecules popping out of the column on the finish of the column.
There are a number of kinds of detectors current in fuel chromatography like:
- Flame ionisation detector (FID)
- Thermal conductivity detector (TCD)
- GS/MS
Engaged on Gasoline Chromatography
The pattern to be separated is ready by mixing with an applicable unstable solvent comparable to heptane, acetone or methanol. The pattern is injected into the injecting port.
The injection port temperature stays 20-50 levels larger than the column. This permits the speedy volatilisation of the pattern.
The cellular fuel is then launched into the column, and the pattern begins.
The constituents separate in response to their respective boiling factors.
Detection of leads to Gasoline chromatography
As quickly because the samples run through column, the detector detects the elute. After it sends the indicators to the pc to generate a peak.
They offer a peak in regards to the retention time of the pattern.
The world beneath the height provides details about the focus of the pattern.
Understanding Gasoline Chromatography with instance
Suppose if we run three samples,
- Containing methanol: Pattern 1
- Containing acetone: Pattern 2
- Unknown: Pattern 3
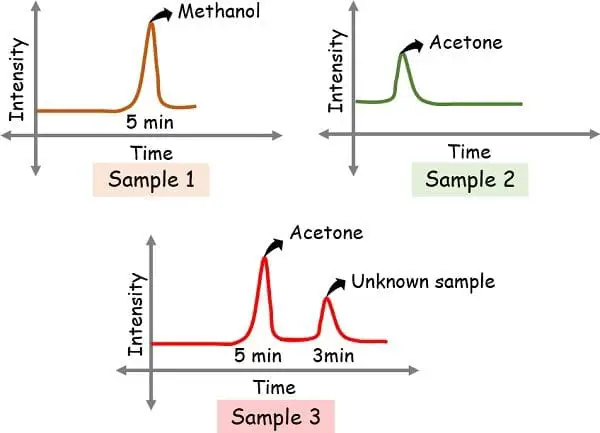
The height in methanol got here at 5 min whereas that of acetone got here at 3 min.
So, when the unknown pattern reveals the height at 5 min and eight min, then it makes it confirms that the one obtained at 5 min is methanol. And, because the graph signifies no peak at 3 min, this means the absence of acetone.
What’s Liquid Chromatography?
Liquid chromatography is essentially the most superior kind of chromatography which makes use of liquid as its cellular section. Presently, liquid chromatography refers to high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Because the title suggests, excessive efficiency means excessive decision, whereas liquid chromatography signifies the liquid cellular section. Furthermore, HPLC is known as high-pressure liquid chromatography in some locations since it really works beneath very excessive strain.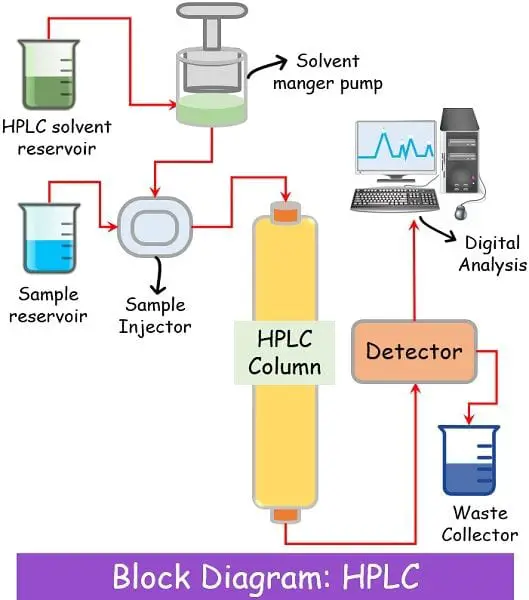
Precept Behind Liquid Chromatography
The working precept of Liquid chromatography or HPLC is that of others. The precept begins with equilibration, the place the column is equilibrated with buffer adopted by pattern binding, wash, and in the end elution.
Varieties of HPLC
There are two main kinds of HPLC primarily based on the polarity of stationary and cellular phases:
- Regular section: The cellular section is non-polar whereas stationary is polar.
- Reverse section: The cellular section is polar, and the stationary section is non-polar.
Parts of Liquid Chromatography
Column
The column is tightly full of small-sized (2 to 50 microns) adsorbing materials. The columns have such a design that they will work effectively beneath high-pressure situations that may vary from 50-350 bar. The fabric used for constructing the columns is kind of sturdy in order to bear the excessive strain.
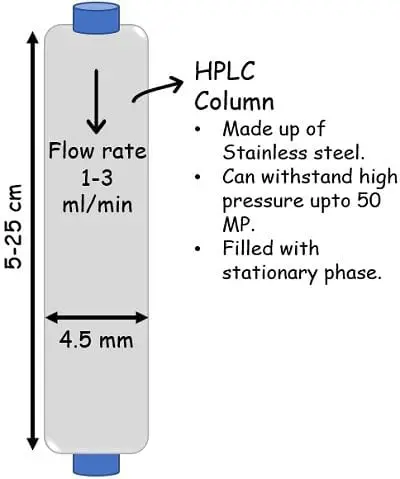 There are three sorts of a column:
There are three sorts of a column:
- Affinity column
- Gel filtration column
- Ion trade column
Stationary Section
The HPLC column consists of adsorbent supplies like silica, hydroxyapatite media, or polystyrene resins/beads. Instance: Polystyrene divinylbenzene.
Beads with smaller diameter leads to improved separation with elevated decision. It’s because it supplies bigger floor areas for the pattern molecules to work together.
Cellular Section
This system makes use of a combination of various solvents as a cellular section.
The number of the cellular section relies on the kind of pattern you might be separating.
There’s a separate cellular reservoir to retailer the cellular section liquid. This reservoir stays hooked up to a pump that pushes the cellular into the column with excessive strain.
Detector
Like fuel chromatography, various kinds of detectors stay hooked up on the finish of the column for an evaluation of the elute popping out.
Some frequent detectors are:
- IR detector
- UV detector
- Fluorescence detector
- Mass spectrometer
- Refractive index detection
- Electrochemical detectors
Understanding Liquid Chromatography with Instance
As a way to detect the constituents of the pattern, you want a typical reference to match. Thus, the identified samples are run for reference.
For instance, we had run samples 1 glucose and a pair of sucrose as identified references and obtained the height at 5 min and eight min. After which we had run pattern 3 as unknown.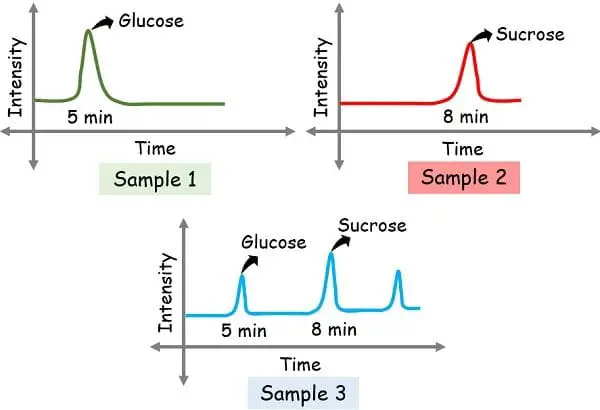
After operating the unknown the peaks obtained at 5 min and eight minutes verify the presence of glucose and sucrose respectively.
Key Variations Between Gasoline and Liquid Chromatography
- The fuel chromatography separates and analyses compounds of their unstable section. In distinction, liquid chromatography is beneficial for partitioning constituent molecules in a soluble state.
- The cellular section is fuel within the case of fuel chromatography. Compared, the cellular section is liquid in liquid chromatography.
- The stationary section will be liquid or fuel in fuel chromatography. Compared, that’s strong adsorbing materials in liquid chromatography.
- The column is lengthy and slender, packed or capillary in fuel chromatography. Whereas the column is brief and extensive; packed columns.
- Gasoline chromatography works beneath excessive temperature, whereas liquid chromatography works beneath excessive strain.
- The fuel chromatography approach is a relatively low-cost affair. However the liquid chromatography is very costly.
Conclusion
The publish will present the important thing variations between fuel and liquid chromatography together with an in depth overview of their parts, working mechanisms and detection.
[ad_2]