[ad_1]
SNP (Single nucleotide polymorphism) and mutation are each associated to the structural modifications within the genome. Whereas researching, folks typically use these two phrases interchangeably. Nevertheless, scientifically, one have to be very cautious whereas utilizing them.
All of the people apart from the twins have their very own model of genome sequences. These variations are primarily because of the SNPs. The probabilities of incidence of SNP are approximated as one per thousand base pairs.
SNP signifies the situation the place one particular person possesses a nucleotide “A” at a particular place P in his genome. However one other particular person can have nucleotide “B” at that very same location P.
Speaking about mutations, they’re truly sudden however regularly occurring modifications within the pure genome. It refers back to the alteration of the gene at some particular places.
They will happen naturally or can get stimulated by sure brokers known as mutagens. The mutation may cause some undesirable modifications within the physique which may result in some potential problems.
This publish will enable you be taught extra about the important thing variations between SNP and mutations intimately.
Content material: SNP Vs Mutation
Comparability Chart
| Foundation of Traits | SNP | Mutations |
|---|---|---|
| Which means | The SNP stands for single nucleotide polymorphism. It refers back to the naturally occurring variation of a single nucleotide at a specific place in a genome. Every variation is liable for the variety inside the inhabitants as much as an considerable diploma |
The transmissible alterations within the construction of the genome by substitution, addition, duplication or deletion of a particular of 1 or a number of nucleotides, thereby resulting in the variable type of the unique genome |
| Frequency of Prevalence | The frequency of the variations in SNPs is greater than 1 % inside the inhabitants | They not often happen, and the frequency of variation is decrease than 1 % inside the inhabitants |
| Quantity of variation | Quantity of variation Alteration or change in a single base unit. | It may be both a change in a single or many nucleotides |
| Rationalization | It’s a naturally occurring historic kind of change | They’re novel compared to the SNPs and are thought of step one towards the evolution |
| Penalties | Related to the issues like coronary heart ailments, diabetes, blood strain, and migraine | Causes the well being points like beta-thalassemia, sickle cell anaemia, cystic fibrosis and many others. |
What’s SNP?
The human genome roughly includes 4-5 million SNPs occurring as soon as in 1000 bp in each particular person. Within the human inhabitants, there are about 100 million kinds of SNPs have been detected to date.
SNP or single nucleotide polymorphism is the alteration of the bottom pair at a single place in a DNA sequence. It refers back to the sort of polymorphism that means the presence of a couple of type of DNA. They’re liable for the distinctiveness among the many people within the inhabitants.
The DNA sequence consists of a sequence of 4 nucleotide bases: A, C, G and T. These 4 stay organized in a correct sequence. So, wherever there’s an alteration at a single place, it signifies SNPs.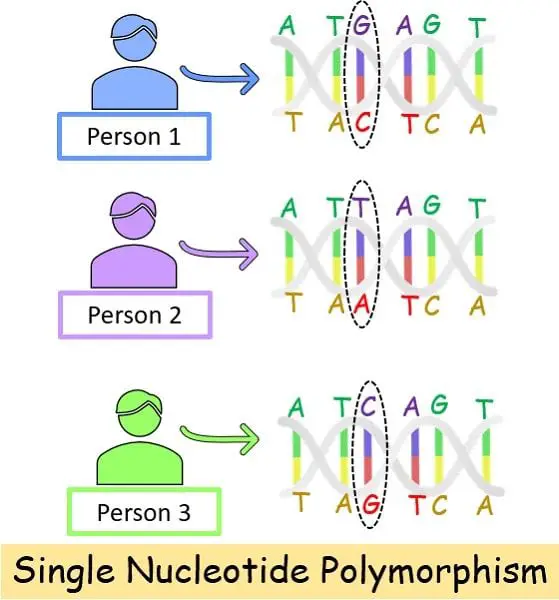
As an example, if the genetic sequence of the overall inhabitants is:
A C T A G T A C G A A G G C T
Then the sequence of the person with SNP is:
A C T A G T A C T A A G G C T
Ailments associated to SNP
The SNP is related to a number of complicated diseases akin to cardiac problems, most cancers, blood strain, diabetes, migraine, Alzheimer, schizophrenia and many others.
Place of SNP
The SNPs mendacity within the non-coding area hamper the construction of mRNA, thereby rising the illness susceptibility. Researchers use them as organic markers for finding genes linked to the illness. Additionally, they’re helpful within the STR-based DNA fingerprinting strategies.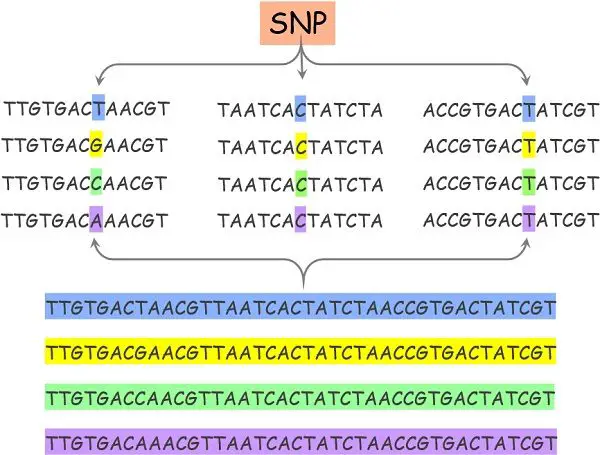
Whereas the SNP current within the coding area may be of two varieties:
- Synonymous substitution: Right here, the amino acid sequence doesn’t change.
- Non-synonymous substitution: This may be both missense or nonsense.
Benefits of SNP
- These days, trendy analysis strategies exploit SNPs as the most recent technology of markers, primarily used within the strategies like genetic mapping and GWAS.
- Because of the change in just one nucleotide, they’re plentiful in quantity.
- We are able to kind SNP by strategies not involving gel electrophoresis.
- The SNP-based evaluation is fast because it relies on oligonucleotide hybridization evaluation.
Disadvantages of SNP
- The SNPs are incapable of manifesting any variability in a household line.
- They’re exhausting to seek out even with trendy strategies. It’s because the vary of variability could be very mild.
What’s Mutation?
A mutation is an occasion that produces an altered type of a gene. It offers rise to the hereditable alterations within the genotype of an organism. Each time we see a immediately occurring trait in a inhabitants, the rationale behind it’s mutation.
It’s believed that mutation was step one towards evolution. The mutation had performed an important half within the majority of variations present inhabitants.
Definition of Mutation
A Dutch Botanist named Hugo De Vries was the one who put ahead the novel idea of mutation in his research. In 1901, he launched the time period mutation and outlined it as “Sudden alteration within the construction of a gene or a chromosome.”
One other scientist named Dobzhansky, who studied mutation, outlined it as “a mistake or misprint within the genetic make-up throughout cell division”.
What does mutation do?
The modifications precipitated within the genome by the mutation mainly change the looks of the gene. This in the end results in the alteration of the characters or genetic messages beneath its management.
The genes are liable for carrying the traits from one technology to a different. They’re exceedingly steady models which can be copied precisely the identical throughout cell division. There are probabilities of errors throughout this course of because of mutation.
Mutation produces an altered gene known as a mutant. The organism bearing the unaltered gene is termed as wild kind.
Varieties of Mutation
We are able to divide the mutations into two most important classes:
A. Level Mutation: This mutation happens by changing a single base pair with one other.
Level mutations are 4 distinguished varieties:
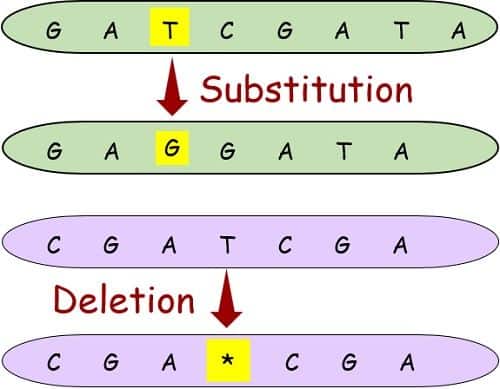
a. Base Substitution: Right here, one base will get changed by one other.
b. Base Deletion: One of many bases will get deleted, inflicting the empty house at that spot.
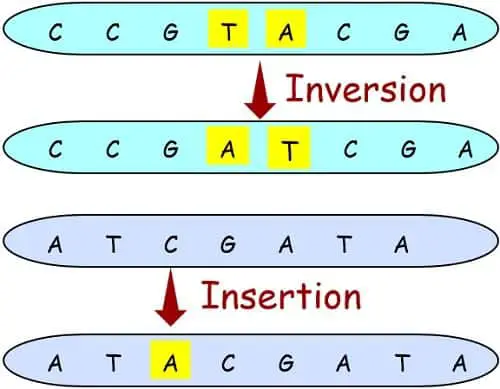
c. Base Inversion: Right here, there’s the reversal of the bottom sequence.
d. Base Insertion: On this mutation, a brand new base pair will get inserted into the genetic sequence.
Penalties of Level Mutation
a. Silent Mutation: Right here, the mRNA codon accommodates the modified base, which additionally codes for a similar amino acid.
b. Missense Mutation: The modified codon codes a totally completely different amino acid.
c. Nonsense Mutation: Typically, the altered codon turns into nonsense or a termination codon.
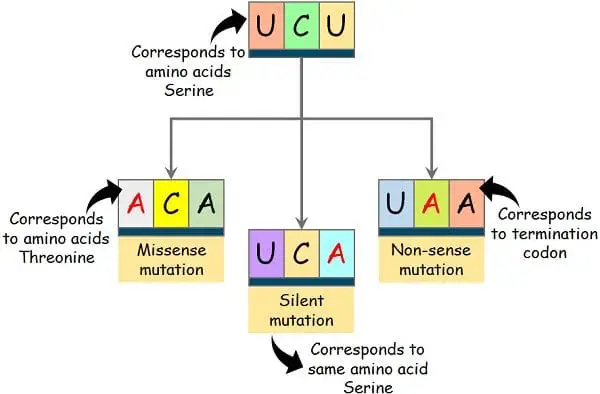
As an example:
UCU codes for serine.
UCU → UCA → Codes for Serine → (Silent mutation)
UCA → ACA → Codes for Threonine → (Missense mutation)
UCA → UAA → Termination codon→ (Non-sense mutation)
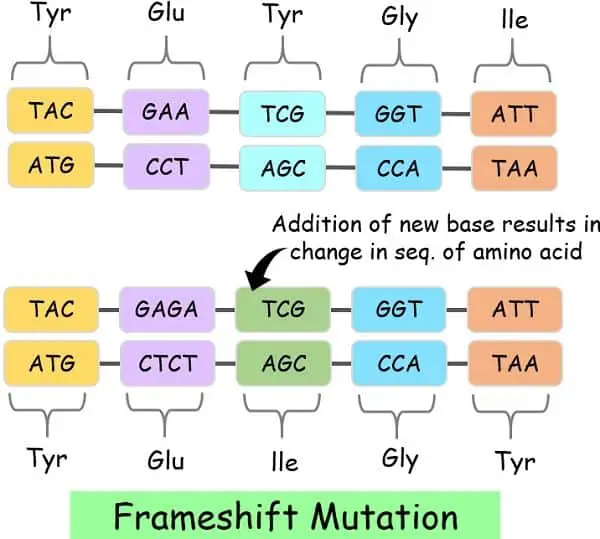
B. Body-shift Mutation: It happens when a number of base pairs shift from their unique locations, altering the complete framework of the genetic sequence.
Key Variations between SNP and Mutation
- The SNP is just a change in a single base sequence at a particular place that results in an considerable diploma of variation within the genome of a inhabitants.
Compared, mutation refers back to the induced alteration of 1 or a couple of base pair within the genetic construction. - The SNPs happen naturally in any inhabitants, whereas the mutations get stimulated by bodily or chemical brokers known as mutagens.
- The frequency of incidence of an SNP is greater than 1% all through the inhabitants. Comparatively, the probabilities of mutation are uncommon, i.e., decrease than 1% inside the inhabitants.
- Solely the alteration of single nucleotides takes place within the case of SNP. However the mutation generally is a results of an alteration of 1 or a couple of bases.
- The SNP is current from the historic occasions that have been liable for some seen modifications amongst any inhabitants. Compared, mutations are a relatively novel idea. Individuals consider mutation to be step one towards evolution.
Conclusion
This publish illustrates the most important variations between SNP and Mutation with the assistance of a comparability chart, associated info and diagrams.
[ad_2]