
[ad_1]
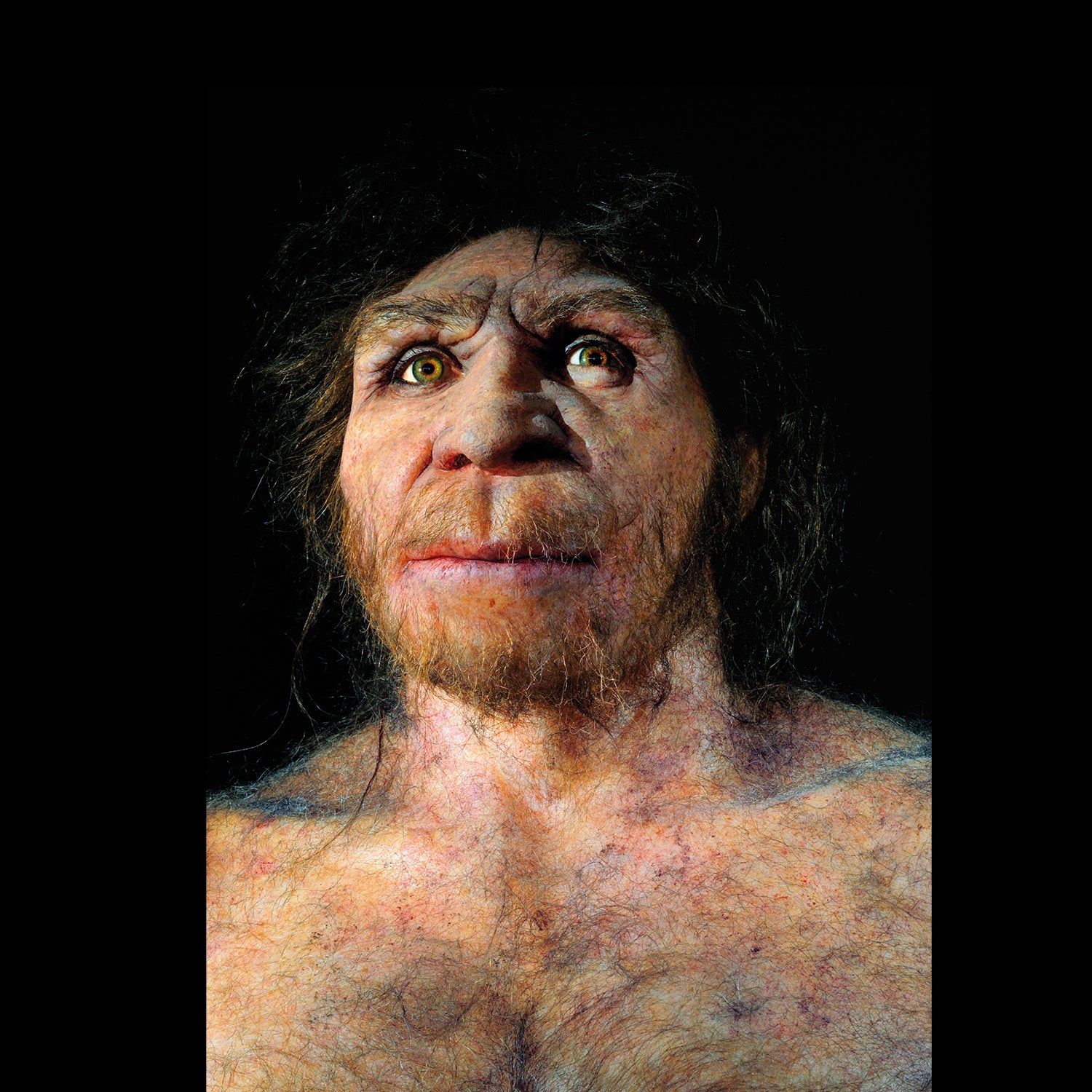
Human ancestors in Africa have been pushed to the brink of extinction round 900,000 years in the past, a examine exhibits. The work, printed in Science, suggests a drastic discount within the inhabitants of our ancestors properly earlier than our species, Homo sapiens, emerged. The inhabitants of breeding people was lowered to simply 1,280 and didn’t develop once more for an additional 117,000 years.
“About 98.7% of human ancestors have been misplaced,” says Haipeng Li, a inhabitants geneticist on the College of Chinese language Academy of Sciences in Beijing, who co-led the examine. He says that the fossil document in Africa and Eurasia between 950,000 and 650,000 years in the past is patchy and that “the invention of this bottleneck could clarify the chronological hole”.
Nick Ashton, an archaeologist on the British Museum in London, who wrote a associated perspective, says he was intrigued by the tiny measurement of the inhabitants. “This could indicate that it occupied a really localized space with good social cohesion for it to outlive,” he says. “Of higher shock is the estimated size of time that this small group survived. If that is appropriate, then one imagines that it might require a steady surroundings with ample assets and few stresses to the system.”
Clues from fashionable DNA
To make their discovery, the researchers wanted to invent new instruments. Advances in genome sequencing have improved scientists’ understanding of inhabitants sizes for the interval after fashionable people emerged, however the researchers developed a technique that enabled them to fill in particulars about earlier human ancestors. Serena Tucci, an anthropologist at Yale College in New Haven, Connecticut, says that such work was sorely wanted. “We nonetheless know little or no concerning the inhabitants dynamics of early human ancestors for a number of causes, together with methodological limitations and difficulties in acquiring historic DNA knowledge from outdated Homo specimens,” she says.
The researchers’ methodology allowed them to reconstruct historic inhabitants dynamics on the premise of genetic knowledge from present-day people. By establishing a posh household tree of genes, the group was in a position to look at the finer branches of the tree with higher precision, figuring out vital evolutionary occasions.
The approach “put the highlight on the interval 800,000 to at least one million years in the past — for which there’s a lot unknown — in a approach that hasn’t been completed earlier than,” says Stanley Ambrose, an anthropologist on the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
This era was a part of the Early-Center Pleistocene transition — a time of drastic local weather change, when glacial cycles grew to become longer and extra intense. In Africa, this led to lengthy intervals of drought. Li says that the altering local weather may need worn out human ancestors and compelled new human species to emerge. Finally, these may need advanced into the final frequent ancestor of contemporary people and our extinct family, the Denisovans and Neanderthals.
Round 813,000 years in the past, the inhabitants of pre-humans started to swell once more. How our ancestors managed to outlive, and what allowed them to flourish as soon as extra, stays unclear, says Ziqian Hao, a inhabitants geneticist on the Shandong First Medical College and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences in Jinan, and a co-author of the paper. Nonetheless, he says that the bottleneck is more likely to have had a vital impression on human genetic variety, driving many necessary options of contemporary people, comparable to mind measurement. He estimates that as much as two-thirds of genetic variety was misplaced. “It represents a key time period in the course of the evolution of people. So there are numerous necessary inquiries to be answered,” he says.
Ashton want to see the researchers’ findings backed by extra archaeological and fossil proof. The authors “counsel that the bottleneck was a world crash in inhabitants”, he says, “however the variety of archaeological websites exterior Africa means that this isn’t the case. A regional bottleneck may be extra possible.”
This text is reproduced with permission and was first printed on August 31, 2023.
[ad_2]