
[ad_1]
Supplies scientists goal to develop autonomous supplies that perform past stimulus responsive actuation. In a brand new report in Science Advances, Yang Yang and a analysis group within the Heart for Bioinspired Vitality Science on the Northwestern College, U.S., developed photo- and electro-activated hydrogels to seize and ship cargo and keep away from obstacles on return.
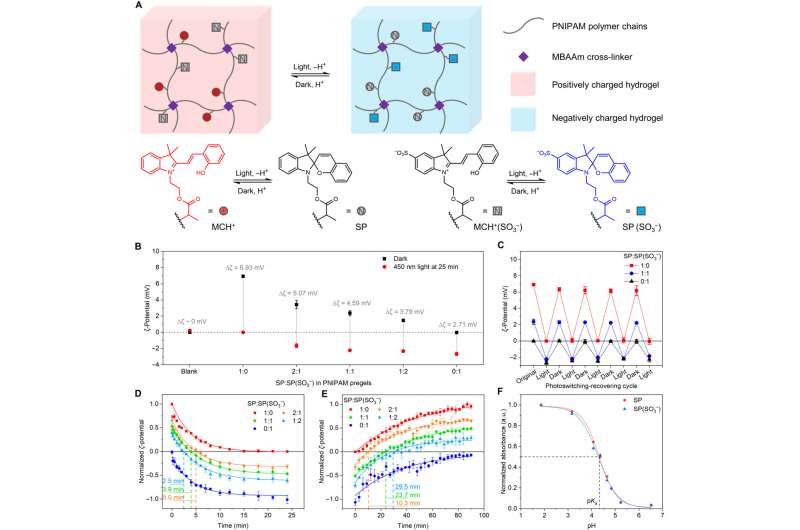
To perform this, they used two spiropyran monomers (photoswitchable supplies) within the hydrogel for photoregulated cost reversal and autonomous behaviors beneath a continuing electrical subject. The photograph/electro-active supplies might autonomously carry out duties based mostly on fixed exterior stimuli to develop clever supplies on the molecular scale.
Bioengineering a charged hydrogel
Delicate supplies with life-like performance have promising purposes as clever, robotic supplies in complicated dynamic environments with significance in human-machine interfaces and biomedical gadgets. Yang and colleagues designed a photo- and electro-activated hydrogel to seize and ship cargo, keep away from obstacles, and return to its level of departure, based mostly on fixed stimuli of seen gentle and utilized electrical energy. These fixed situations offered vitality to information the hydrogel.
The analysis group covalently built-in spiropyran moieties with various substituents into the constructs to control the web cost of the mushy supplies. They used finite component simulations to information the design and motion of the charged hydrogels and engineer 3D floor profiles to maximise the dielectrophoretic impact. Yang and the group additional studied the scope of electroactive locomotion and photoactuation within the spiropyran hydrogels.
Cost reversal of spiropyran-functionalized polymers
Yang and colleagues used two completely different spiropyran molecules with completely different web prices. They synthesized every of the molecules with a polymerizable methacrylate group based mostly on present stories.
They included completely different ratios of the spiropyran molecules into N-isopropylacrylamide polymer chains (PNIPAM) to type hydrogels. On this occasion, they tuned the cost reversal functionalities utilizing copolymers of the spiropyran structural items to point out photoswitchable potential and cost reversible behaviors with tunable cost. The scientists tuned the cost reversal time by altering the ratio of the 2 spiropyran moieties, with out altering the switching and restoration charges.
Photograph-activated electroactive movement of the spiropyran-PNIPAM hydrogels
Based mostly on cost reversal habits of the polymers, Yang’s group photoregulated the electroactive hydrogels by utilizing a crosslinker to organize them.
At first, the group might positively cost the hydrogel to maneuver in direction of the cathode beneath a direct present electrical subject, the place the constructive cost transferred from the spiropyran moieties into the hydrogel community. Thereafter, the completely certain sulfonate teams on the polymer chain made the web cost of the assemble adverse, permitting the negatively charged hydrogel to navigate again to the anode.
The group studied the photoregulated electroactive locomotion speeds of the hydrogel disks throughout a number of light-dark cycles to look at their locomotion pace, and decided the connection between the cost and pace of the hydrogel disks. They based mostly this on the stability between the electrostatic power and hydrodynamic drag power, the place the upper utilized voltage and bigger diameter of the hydrogel disks delivered greater locomotion pace. Such polymeric gadgets are well-suited to seize and ship cargo by means of autonomous looking.
Capturing and delivering cargo
Yang and colleagues explored the cargo supply potential of the constructs by engineering easy disk-shaped spiropyran-PNIPAM hydrogels and sphere-shaped constructs embedded with nanoparticles as cargos. The robust dielectrophoretic power allowed the supplies to endure autonomous looking and choosing up features.
Based mostly on simulations, Yang and colleagues shaped a 3-arm spiropyran PNIPAM hydrogel object utilizing photoinitiated free radical polymerization with superior seize functionality of the cantilever arms. When uncharged, the electrical subject gradient across the hydrogel vanished, enabling autonomous cargo launch throughout cost reversal. The cargo launch additionally occurred by turning off the electrical subject.
-
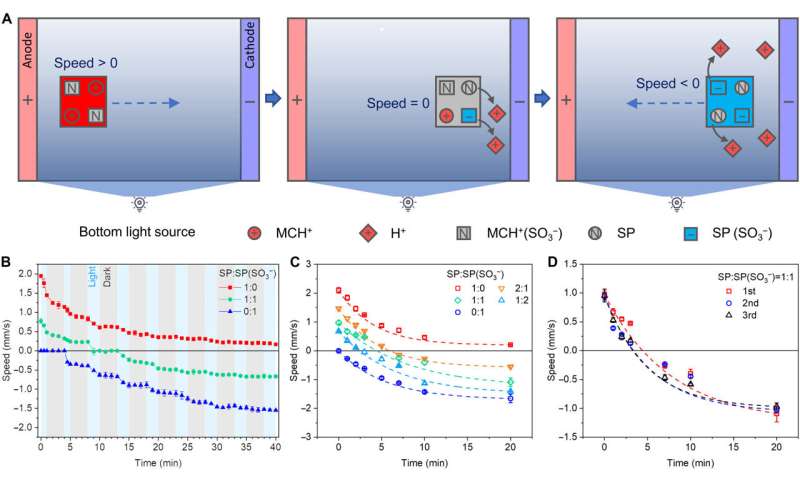
Photoregulated electroactive locomotion of the spiropyran-PNIPAM hydrogels. (A) Schematic illustration of the photoregulated electroactive locomotion of SP/SP(SO3−) spiropyran-PNIPAM hydrogels with the power to swim towards the cathode that navigate again to the anode autonomously beneath fixed stimuli of electrical subject and light-weight irradiation. The dashed arrows point out the locomotion course of the hydrogel; the curved arrows point out the cost trade between the hydrogel and the answer. (B) Electroactive locomotion pace of the spiropyran hydrogel discs throughout serial cycles of sunshine (blue, 1 to 2 min) and darkish (grey, 3 min) durations. (C) Locomotion pace of spiropyran hydrogel discs versus time of sunshine irradiation (0.95 mW/cm2) for various SP/SP(SO3−) molar ratios after in a single day incubation in 5 mM HCl. (D) Repeated locomotion pace measurements of spiropyran hydrogel discs with the SP/SP(SO3−) molar ratio of 1:1. Every measurement was carried out after a two-hour interval of darkness of the hydrogel in 5 mM HCl. The reference curves are fitted with an exponential perform. Error bars signify the SD of the information collected from 0.3-s locomotion trajectory throughout a uniform movement interval with a 0.1-s interval. Credit score: Science Advances, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4566
-
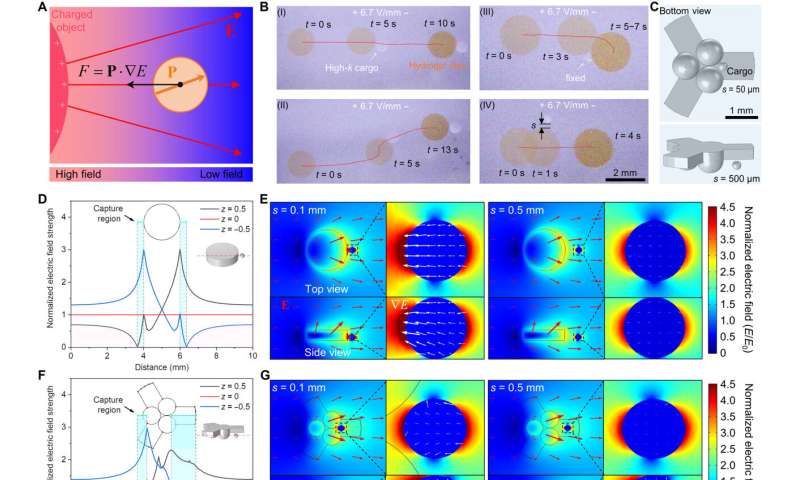
Seize and supply of high-k cargo utilizing DEP forces. (A) Schematic illustration displaying a high-k particle subjected to a DEP power towards the areas with greater subject magnitudes beneath a nonuniform electrical subject induced by a charged object. (B) Seize and supply of high-k cargo by the disc-shaped spiropyran-PNIPAM hydrogel with the SP/SP(SO3−) molar ratio of 1:1 together with (I) rectilinear supply, (II) looking and choosing up, (III) cease by a hard and fast cargo, and (IV) failed seize of the cargo at a far distance s. (C) Schematics of three-arm robot-like hydrogel. (D) Finite component calculation of normalized electrical subject energy alongside the reference line by means of the middle of the disc-shaped hydrogel with the normalized ζ-potential z = −0.5, 0, and 0.5. The seize areas are highlighted in gentle blue, and the repulsive DEP area is highlighted in gentle purple. (E) The normalized electrical subject energy map, subject vector E (purple arrows), and subject gradient ∇E (white arrows) felt by the high-k particle on the distance s = 0.1 mm (left) and 0.5 mm (proper) for the disc-shaped hydrogel. (F) Finite component calculation of normalized electrical subject energy alongside the reference line by means of the middle of the three-arm hydrogel object with z = −0.5, 0, and 0.5. (G) The normalized electrical subject energy map, subject vector E (purple arrows), and subject gradient ∇E (white arrows) felt by the high-k particle on the distance s = 0.1 mm (left) and 0.5 mm (proper) for the three-arm hydrogel. (H and I) Calculated DEP power brought on by the high-k particle versus the gap s and the normalized ζ-potential z. (J) Autonomous seize of a high-k cargo in both place (I) P1 or (II) P2 of a 1:1 SP/SP(SO3−) robotic and (III) supply of cargo when the hydrogel object returns after 7 min of irradiation. Credit score: Science Advances, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4566
Robotically avoiding obstacles
The analysis group confirmed how supplies with a excessive dielectric fixed induced a gorgeous electrophoretic power, and supplies with a decrease dielectric fixed exerted a repulsive electrophoretic power on the adjoining charged hydrogel object.
Utilizing finite component calculations, they confirmed the potential of low dielectric constants to information the charged hydrogel by means of obstacles. Below fixed stimuli of the electrical subject and light-weight irradiation, the hydrogel routinely bypassed boundaries and traveled again after cost reversal, with out human intervention.
Outlook
On this means, Yang and colleagues designed a photo- and electroactive hydrogel that may cargo seize and ship, in addition to keep away from obstacles beneath fixed exterior stimuli. The scientists used two completely different ratios of spiropyran moieties within the hydrogel and facilitated the web cost within the chemically random community to be tunable beneath irradiation with blue gentle. This enabled photoregulated, electroactive movement with autonomous habits beneath the course of sunshine and electrical energy.
The autonomous mushy matter merchandise elegantly captured and delivered cargo whereas avoiding obstacles with purposes fitted to situations to make sure the protection of monitoring a state of affairs from afar—as an example, the place human intervention is impractical. These new biomaterials with autonomous performance will be resourcefully engineered utilizing environmentally delicate electrostatic interactions and photoactuation in mushy supplies.
Extra data:
Yang Yang et al, Autonomous hydrogel locomotion regulated by gentle and electrical fields, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4566
Anne Helene Gelebart et al, Making waves in a photoactive polymer movie, Nature (2017). DOI: 10.1038/nature22987
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Hydrogel locomotion regulated by gentle and electrical fields (2023, August 22)
retrieved 22 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-hydrogel-locomotion-electric-fields.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]