
[ad_1]
Of the eight morphologically equivalent however genetically distinct G. duodenalis assemblages A-H, virtually all human infections are attributable to assemblages A and B. Curiously, current proof suggests there could also be marked variations within the forms of and diploma of pathology skilled by these contaminated with both G. duodenalis assemblages A and B, in addition to between these burdened with single-assemblage (A or B) or mixed-assemblage (A and B) infections. We investigated this utilizing stool samples offered by school-aged youngsters located alongside the southern shoreline of Lake Malawi, Malawi.

Southern shore of Lake Malawi. Taken by John Archer.
Human giardiasis is a globally necessary intestinal parasitic illness attributable to the eukaryotic protozoan Giardia duodenalis (syn. Giardia intestinalis, Giardia lamblia). This parasite is primarily thought of a waterborne pathogen that has a direct faecal-oral life cycle. As such, solely a definitive host is required for efficient transmission.
While cosmopolitan in distribution, prevalence of human giardiasis will be significantly excessive in rural areas of low- and middle-income nations (LMICs) the place sufficient water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) infrastructure is missing, together with these in sub-Saharan Africa. In these areas, human giardiasis predominantly afflicts youngsters < 15 years of age, which may severely influence childhood improvement. Of the eight recognized morphologically equivalent however genetically distinct assemblages of G. duodenalis, virtually all human infections are attributable to assemblages A and B. Curiously, nevertheless, current proof suggests there could also be marked variations within the varieties and diploma of pathology skilled by these contaminated with both G. duodenalis assemblages A and B, in addition to between these burdened with single-assemblage (A or B) or mixed-assemblage (A and B) infections.
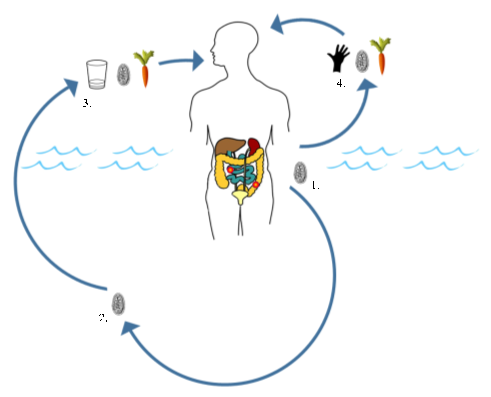
We investigated this in a current publication, the place major faculty youngsters attending 4 faculties in shut proximity to the southern shoreline of Lake Malawi (Mangochi District, Malawi) had been surveyed.
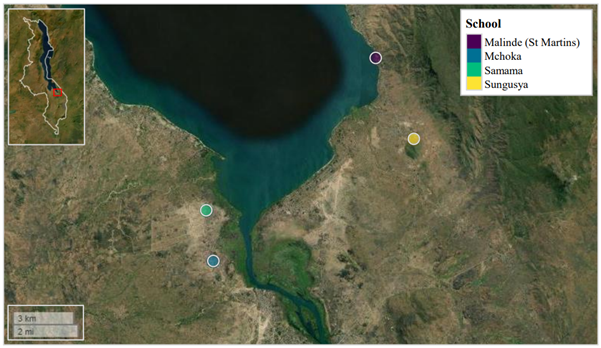
Lake Malawi is considered one of seven African Nice lakes. With a water floor space of ~29,600 Km2, the lake occupies roughly one-fifth of Malawi, while additionally bordering Tanzania and Mozambique alongside its jap shoreline. The lake’s most southern shoreline borders Mangochi District. Owing to inadequate WASH infrastructure, many members of Mangochi’s a number of communities depend on the lake as a supply of consuming water, meals (by way of fishing), a spot to wash and have a tendency livestock, and for recreation. As such, human water-contact with the lake’s shoreline is commonplace, leading to a excessive prevalence of waterborne illnesses on this space, reminiscent of urogenital and intestinal schistosomiasis.
Methodology
Stool samples had been offered by 305 school-aged youngsters. A proportion of every stool was used to hold numerous point-of-care diagnostic analyses together with Kato-Katz faecal microscopy and QUIK CHEK speedy diagnostic checks (RDTs) to diagnose an infection with giardiasis, and faecal occult blood/faecal calprotectin RDTs to evaluate the presence of overt blood and calprotectin throughout the stool (a measure of intestinal pathology). A proportion of every stool was additionally saved in ethanol for transportation to the Liverpool College of Tropical Medication (LSTM) for future DNA extraction and molecular evaluation. Intestinal pathology knowledge had been additionally collected by way of questionnaire; every examine participant that offered stool additionally responded to the questions ‘do you at the moment have belly (abdomen) ache?’ and ‘do you at the moment have free stool (diarrhoea)?’.
Again on the LSTM, DNA was extracted from all faecal samples utilizing a bead-beating step to liberate DNA from any potential helminth (worm) eggs and protozoan cysts. A diagnostic 18S real-time PCR was then carried out to measure prevalence.
Outcomes and perspective
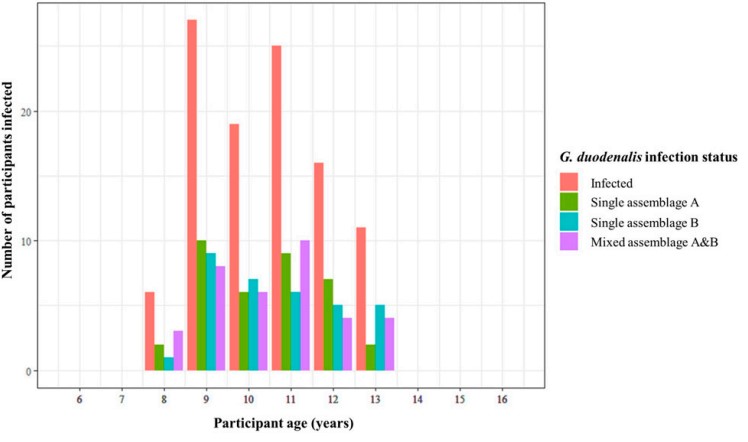
The diagnostic real-time PCR confirmed the prevalence of G. duodenalis an infection to be 39.3% inside this examine cohort, a reasonably typical prevalence of giardiasis an infection in settings reminiscent of these. Utilizing all samples optimistic for G. duodenalis an infection (120), an endpoint nested PCR focusing on the G. duodenalis beta-giardin (bg) gene was then carried out (profitable in 108 of those 120 samples). The amplified bg fragment was sequenced from all 108 samples, that means the infecting G. duodenalis assemblage(s), (A, or B, or each!), could possibly be decided.
We discovered a reasonably equal prevalence of an infection varieties throughout all G. duodenalis infections (G. duodenalis assemblage A solely: 35%, assemblage B solely: 32%, and an infection with each assemblages A and B: 33%). This got here as a little bit of a shock, as in earlier research of this type (of which there are few), a a lot increased prevalence of 1 assemblage (A or B) over the opposite is often discovered. This led theorisation that any discordance in both assemblage being extra (or much less) related to intestinal pathology shouldn’t be a results of one or the opposite assemblage kind being extra pathogenic organisms, however reasonably that it’s maybe the least prevalent assemblage inside a given locality that’s answerable for inflicting intestinal pathology.
Curiously, regardless of a reasonably equal prevalence of an infection varieties, we discovered a statistically vital optimistic affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage B and each self-reporting of abdomen ache and self-reporting of diarrhoea, however no affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage A and any type of intestinal pathology.
With regard to self-reported diarrhoea particularly, these knowledge are in settlement with some earlier research that additionally discovered an affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage B and symptomatic diarrhoea (however no such affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage A and diarrhoea) but are additionally in disagreement with different research that reached the other conclusion.
That is additionally true for self-reported abdomen ache; these knowledge are in settlement with some earlier research which have additionally discovered an affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage B and abdomen or belly ache (however no affiliation between single an infection with G. duodenalis assemblage A and abdomen/belly ache), however disagreement with different research which have once more reached the other conclusion.
No affiliation was discovered between any G. duodenalis an infection kind and faecal-occult blood or faecal calprotectin. These assays, nevertheless, had been deemed poor diagnostic markers of an infection with G. duodenalis when in comparison with the real-time PCR and QUIK CHEK RDTs.
We additionally discovered a optimistic affiliation between combined an infection with each G. duodenalis assemblages A and B and self-reporting of diarrhoea, in addition to a statistically vital affiliation between combined an infection with each assemblages and self-reporting of abdomen ache. Though fascinating observations, conclusions as as to whether these associations are a results of people being contaminated with G. duodenalis assemblage B (doubtlessly extra pathogenic inside this examine group), or whether or not there may be interaction between combined an infection with each assemblages and intestinal pathology, can’t be drawn utilizing these knowledge. As such, extra work is required to scrutinise additional whether or not an infection with each human-infecting G. duodenalis assemblages (A and B) has a extra detrimental influence on intestinal well being than an infection with only one assemblage.
We concluded that molecular surveillance strategies reminiscent of these ought to proceed for use, significantly in areas missing sufficient entry to WASH infrastructure, to higher perceive the detrimental well being impacts, not solely of an infection with G. duodenalis but additionally of poor entry to wash and protected consuming water and sanitation amenities. In doing so, not solely can the pathological influence of human giardiasis be higher understood, however, by improved illness surveillance, management, and entry to WASH infrastructure, a discount in disease-associated pathologies skilled by the world’s most deprived communities can be achieved.
We wish to thank all examine members attending Samama, Mchoka, Sungusya, and Malinde (St. Martin’s) faculties for his or her generosity throughout pattern collections, in addition to all academics and well being staff in Mangochi District for his or her help throughout pattern collections and examine planning.
[ad_2]