
[ad_1]
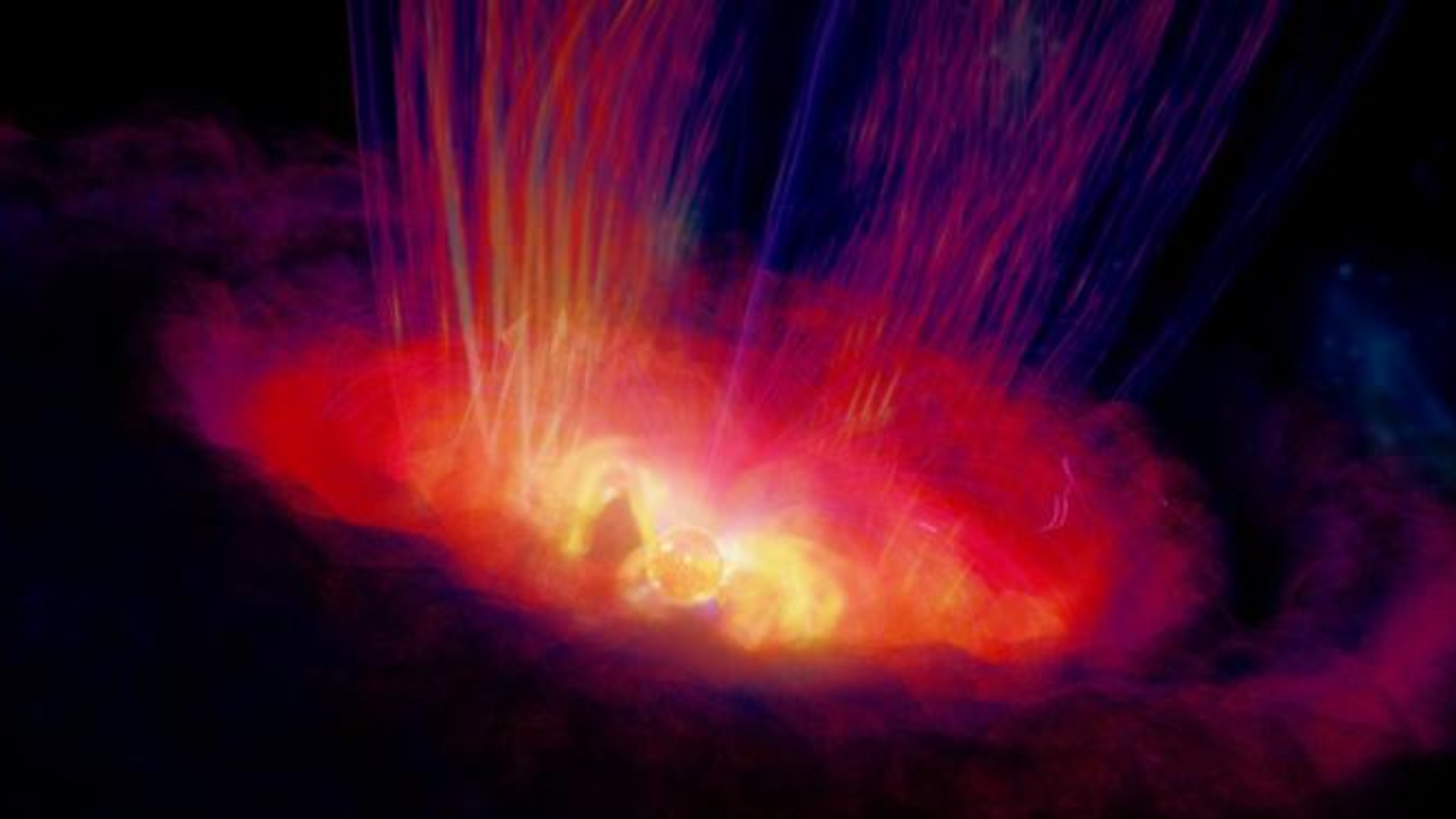
Astronomers have witnessed a younger, sun-like star blasting out high-energy gamma radiation for the primary time.
The remark represents the primary proof that the sort of low-mass star, referred to as a T. Tauri star and surrounded by a planet-forming disk of gasoline and dirt, can emit gamma radiation. In a nutshell, the sort of radiation represents essentially the most energetic type of mild. Down the road, these findings might have essential implications for our understanding of stars and planetary programs throughout their youth.
“This observational proof is crucial for understanding the origin of sources which have beforehand remained unknown for greater than a decade, which is definitely a step ahead in astronomy,” Agostina Filócomo, discovery staff chief and an astronomer on the Universidad Nacional de La Plata, mentioned in an announcement. “It is usually important to grasp the processes that happen through the early phases of star formation: If a T Tauri star produces gamma-ray radiation, it’ll have an effect on the gasoline circumstances of the protoplanetary disk and, consequently, the evolution of planet formation.”
The astronomers captured their observations of this intriguing star with the Fermi satellite tv for pc telescope, which observes the universe in gamma rays. In different phrases, this telescope has the power to gather high-energy radiation knowledge that may be powerful to assemble from the floor of Earth. Fermi has been observing the sky because it launched in 2008, however about 30% of the gamma rays it has seen have but to be attributed to a supply. Thus, Filócomo and her staff set about trying to establish a few of these mysterious sources.
Gamma rays might come from tantrum-throwing toddler stars
The analysis staff mainly discovered that many gamma rays seem to originate from areas with actively forming stars. That is one thing that defied rationalization and thus required deeper investigation, with the staff honing in on the star-forming area NGC 2071.
Specifically, Filócomo and colleagues seemed for T.Tauri stars in NGC 2071, which lies within the northern a part of the molecular cloud Orion B, situated round 1,350 mild years from Earth. T.Tauri stars are notable as a result of they’re usually discovered close to star-forming areas, nonetheless cocooned within the very gasoline and dirt that created them. And since they’re shrouded in these gaseous cradles, T. Tauri stars exhibit fluctuating ranges of brightness — making them a sort of variable star.
The staff recognized three totally different unidentified gamma-ray sources that appeared to be coming from the route of NGC 2071, the place at the least 58 T. Tauri stars are recognized to be at the moment forming. There aren’t any different objects within the area that could possibly be sources of gamma-ray emissions, the researchers reasoned.
The staff thinks T. Tauri stars could possibly be emitting gamma rays sporadically throughout highly effective flare occasions referred to as “megaflares,” which happen when magnetic vitality saved within the atmospheres of younger stars will get launched within the type of highly effective electromagnetic bursts.
This idea is just like the way in which photo voltaic flares are launched by the solar, besides they happen on a radically bigger scale. Megaflares can stretch for distances equal to a number of occasions the radius of the celebrities that launch them within the first place and are so highly effective that, if the solar have been to blast out such an eruption, life on Earth can be threatened.
But regardless of this harmful potential, some scientists argue that megaflares within the early historical past of the photo voltaic system, when the solar was embedded in a disk of gasoline and dirt, could have truly been helpful to planet start by driving gasoline and triggering the formation of pebbles and different small rocky supplies.
As such, not solely might the staff’s findings assist account for beforehand unattributed gamma-ray detections, however might have implications for our understanding of the photo voltaic system — particularly through the interval when our planet was being created.
“The invention of this phenomenon serves to grasp how not solely the solar but in addition our house planet, Earth, have been fashioned and advanced,” Filócomo concluded.
The staff’s analysis was printed Aug. 23 within the journal Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
[ad_2]