
[ad_1]
Quantity electron microscopy (vEM) is a robust offshoot of electron microscopy. It supplies 3D reconstructions of samples at nanometer decision. vEM covers a set of strategies that contain taking a number of sections from a single pattern and imaging them to supply a complete 3D picture. Picture volumes can exceed ten cubic microns and make it attainable to check giant numbers of subcellular buildings and their connectivity.
What should you may see intact buildings inside cells, in three dimensions, with the picture quantity exceeding tens of microns, at nanometer decision?
All of these are attainable with quantity electron microscopy (vEM), a dazzlingly highly effective offshoot of electron microscopy (EM).
Learn on for an introduction to vEM, the way it works, the questions it may well tackle, and a few of its greatest challenges.
What Is Quantity Electron Microscopy?
Merely put, vEM allows us to picture three-dimensional (3D) buildings of organic samples at excessive decision of their native surroundings. The time period describes a variety of electron microscopy strategies that present a 3D picture on the finish fairly than a single linear methodology.
Such a abstract belies its energy, nonetheless. There’s a purpose Nature listed it amongst their applied sciences to observe in 2023, together with titans just like the James–Webb telescope and high-precision radiocarbon relationship.
3D pictures of huge chunks of cells and tissues enable us to see and interrogate networks of subcellular elements. Usually talking, the extra linked subcellular elements (corresponding to mitochondria and synapses) are, the more healthy the cells are. Plus, organelles and molecular complexes affiliate and dissociate with one another and their surroundings in response to their operate.
The reverse can be more likely to be true. Disconnection between subcellular elements may point out pathological states for a given pattern sort—and that is the world vEM lets us discover!
In addition to connectedness, there are different advantages of vEM too. You possibly can analyze a a lot greater space than typical EM strategies however with out compromising on the decision of your knowledge or processing further samples. The elevated imaging space means you’ll be able to picture a number of cells concurrently and select bigger areas of curiosity.
We’ll come to the analysis questions you’ll be able to reply utilizing vEM later, however for now, observe vEM reveals pattern connectedness, texture, and spatial/mobile context.
The important thing phrase right here is connectedness.
vEM originated inside connectomics—learning the mind’s intact structural and practical connections referred to as the connectome—which is difficult to check with conventional 2D imaging strategies.
Fluorescence microscopy precisely captures comparatively macroscopic properties, corresponding to the placement of mobile elements, whereas electron microscopy captures the ultrastructural particulars of a pattern. Nonetheless, each these strategies are often restricted to the horizontal aircraft.
This rationalization is barely simplified—we have now confocal laser scanning microscopy, in spite of everything. However that requires getting your goal to fluoresce by conjugating it to dye or utilizing transgenics. The purpose is vEM is an further 3D imaging method that has its personal key advantages.
Why Do We Want vEM? A Easy Illustration
So why do we want vEM? Sadly, 2D slices and cross-sections by way of 3D shapes can result in deceptive representations of their form.
Try Determine 1 beneath to see what number of cross-sections a dice can generate—it is dependent upon the way you slice it!
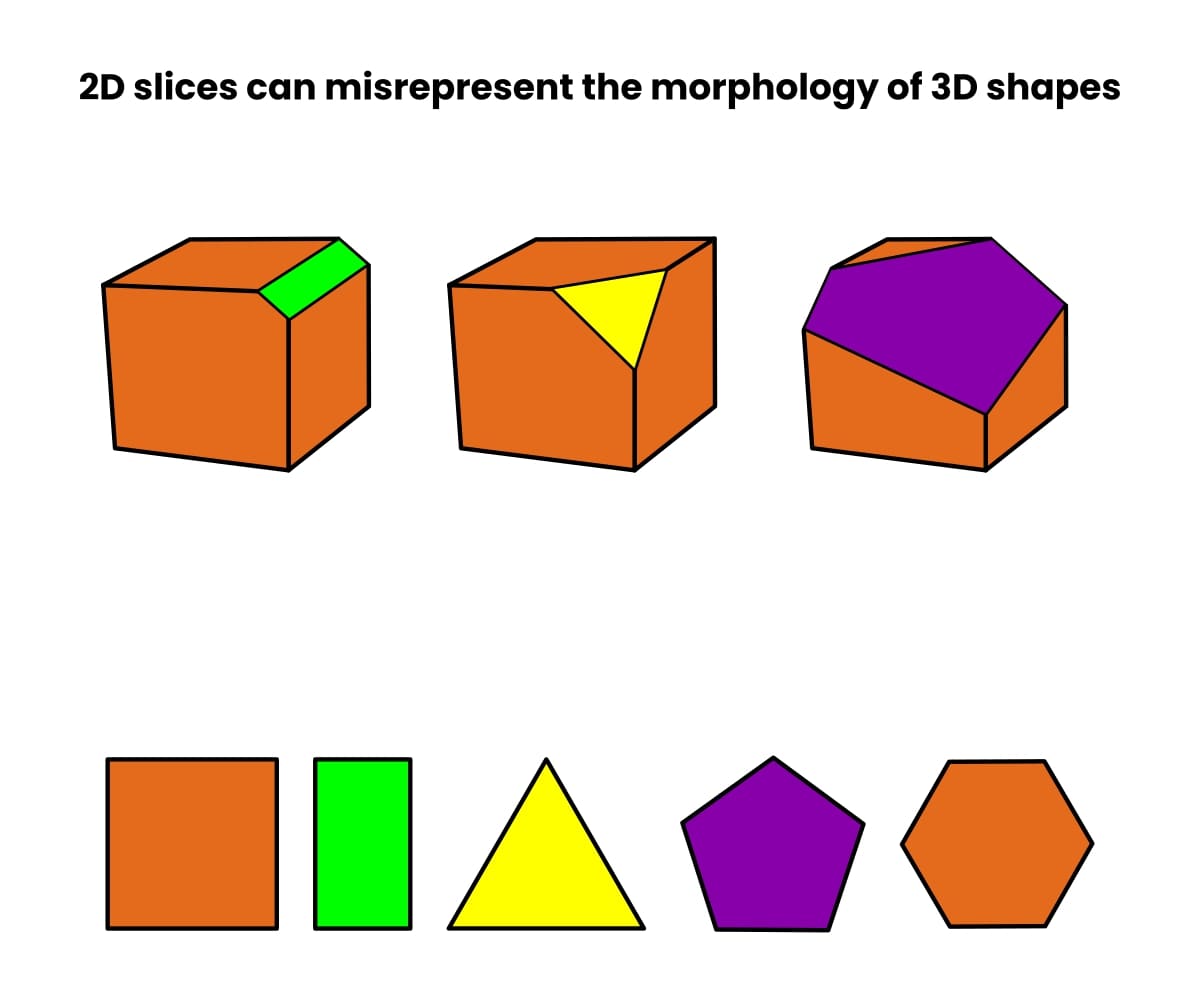
Now think about that, fairly than a dice, you will have an organelle corresponding to a vacuole or mitochondrion. The variety of attainable (and deceptive) cross-sections is sort of limitless.
Then think about that you’re a construction that nobody has ever seen. How are you aware what’s correct?
One answer is to get a 3D picture of the intact construction. And now, with vEM, you’ll be able to!
How Does vEM Work?
Standard electron microscopy strategies often contain sectioning samples into single, ultra-thin slices sectioning samples into single, ultra-thin slices and imaging them.
With vEM, you purchase pictures from a sequence of slices by way of your pattern after which computationally mix them to create the ultimate 3D reconstruction. And what a reconstruction! Try this 3D rendering of a number of linked neurites. [1]
There are three principal methods to generate a number of slices from a pattern for 3D imaging.
1. Array Tomography
Array tomography is the most cost effective strategy.
You repair and part your pattern as you’d for every other electron microscopy strategy, however you generate lots of sections. Then, you organize them right into a ribbon that serves as a ticker tape by way of your pattern.
When you’ve received all of your sections, you picture them serially to create a 3D reconstruction.
Array tomography can be probably the most labor-intensive strategy, however it’s non-destructive, which means you’ll be able to retrieve the sections and picture them utilizing every other modality. It’s additionally suitable with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Learn this text for a fast refresher on the variations between SEM and TEM should you want it, and take a look at this text for a deeper dive into array tomography.
2. Serial Block-Face Scanning Electron Microscopy
The serial block-face (SBF) strategy is much like array tomography. Nonetheless, as an alternative of producing all of the sections in the beginning and imaging all of them in sequence, the sectioning and imaging are iterative. That’s to say, you part, then picture, part, picture, and so forth.
The beauty of SBF is that you could automate it. The Volumescope 2 SEM is a robust, modular vEM answer that incorporates an ultramicrotome contained in the imaging chamber for automated knowledge acquisition!
Nonetheless, in contrast to array tomography, SBF is harmful, which means evaluation by way of different microscopy strategies should come beforehand. Plus, it’s solely suitable with SEM.
3. Targeted Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy
Targeted ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) combines a centered ion beam (often gallium ions) with scanning electron microscopy. Not like serial block-face imaging, FIB-SEM doesn’t contain eradicating sections sequentially. [2]
As a substitute, it makes use of the centered ion beam to erase pattern materials layer by layer to disclose a brand new, deeper floor for imaging at every step. Due to this, it’s harmful.
On the plus facet, utilizing an ion beam to take away pattern materials affords a a lot increased decision within the z course when in comparison with utilizing an ultramicrotome. The z-direction decision will be as excessive as just a few nanometers.
The right way to Determine Whether or not to Use vEM
vEM is wonderful. However must you use it?
The perfect factor to do is sit down together with your native analyst or core facility supervisor and communicate to them concerning the targets of your challenge to resolve whether it is applicable.
vEM takes a very long time (see beneath), and the amenities to do it are uncommon at current, so you should formulate your analysis query nicely and have clear, particular targets.
There are two important standards:
- Your analysis query should be involved with 3D ultrastructures.
- This ultrastructure should confer a change in operate or phenotype.
Listed here are some examples of questions you’ll be able to tackle utilizing vEM:
- Are there adjustments in mobile/organellar form/group below totally different situations?
- Are there adjustments in mobile/organellar connectedness below totally different situations?
- Are there ultrastructural variations in tissues or cells below totally different situations?
- The place do subcellular entities originate, how are they distributed, and the place do they go?
And, as a result of vEM lets you find just about any subcellular element you need (offering you’ll be able to stain it), you can begin to reply deep questions corresponding to:
- How a lot of X is there per cell?
- What’s the whole quantity and mass of X per cell?
- How do these values change below totally different situations?
Maybe the important thing level is apparent—the uncooked knowledge you reply these questions with is a picture, not an summary illustration of your knowledge.
And vEM datasets are extremely wealthy. Plan for this and put together to take the time to research your knowledge fastidiously. Keep in mind that there’ll most likely be extra knowledge than you’ll be able to hope to interpret, and your pictures will doubtless include buildings invaluable to another person’s challenge. Sharing your knowledge is subsequently inspired.
The Electron Microscopy Public Picture Archive is the first on-line repository for 3D pictures and tomograms. Be sure you have a look at among the unimaginable knowledge on it.
The vEM Workflow
So, you will have determined to make the leap and embark on a vEM challenge. What are you able to anticipate?
Earlier than you do something, go to the amount electron microscopy group’s webpage. It hosts coaching movies, protocols, explanations, key folks, information, a Twitter feed—all the things!
Here’s a breakdown of the workflow, key issues, and issues you’ll be able to anticipate. If you happen to’re in a rush, take a look at Determine 2 beneath.
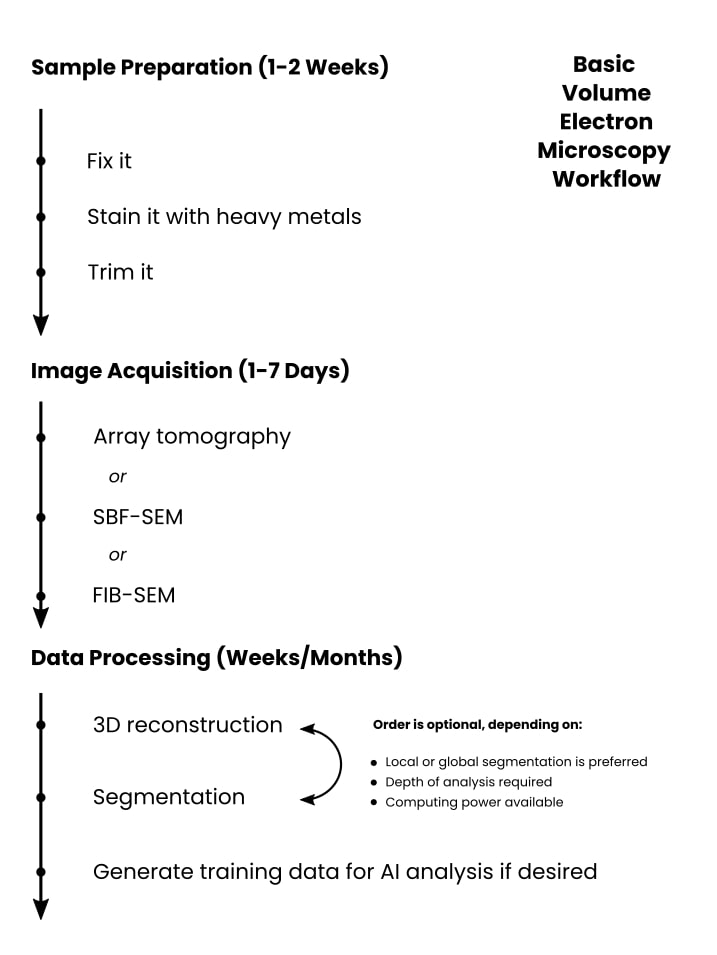
Pattern Preparation (1-2 Weeks)
Pattern prep for vEM has lots in frequent with different EM strategies. You repair your pattern, coat it with a heavy steel stain to offer distinction, then slice it up and picture it.
You’ll need to establish your area of curiosity utilizing a smart strategy corresponding to fluorescence microscopy or micro-computer tomography (micro-CT). Then you definitely’ll transfer on to staining your pattern earlier than embedding it in resin and doing any handbook trimming.
Take care together with your pattern prep, because it largely dictates whether or not your vEM imaging challenge will succeed or fail. We have now a wonderful information to EM pattern prep, and lots of the factors apply to vEM additionally.
And at last, observe that vEM samples are sometimes embedded in a non-conductive resin, so one of many challenges is guaranteeing that your pattern prep ends in conductive samples for imaging.
Picture acquisition (1-7 Days)
As talked about earlier, a key know-how in vEM is SBF imaging, the place your pattern is minimize into sections utilizing an ultramicrotome contained in the imaging chamber of the electron microscope.
In such circumstances, picture acquisition begins by fastidiously aligning the ultramicrotome to work harmoniously with the microscope optics. Then, you set the reducing window and imaging parameters earlier than buying your knowledge.
Presently, vEM devices are giant and costly. The info acquisition doesn’t tolerate pattern motion, so they’re often on anti-vibration flooring and want shielding from electromagnetic interference from surrounding infrastructure (prepare stations, trams, and many others.)
Information Processing (Days, Weeks, or Months)
Upon getting knowledge, it’s worthwhile to course of and interpret it. How lengthy this and your hands-on time will take is dependent upon your analysis targets.
One step you’ll should do, no matter your downstream intentions, is to align your slices to supply the 3D picture.
Past that, it relies upon, as I say, in your targets. In principle, inspecting your closing 3D picture for a sure/no reply to your analysis query ought to be comparatively fast and easy.
However you could must do one thing extra advanced, corresponding to establish areas of curiosity to phase to (say) generate coaching knowledge for a man-made intelligence mannequin. Relying in your pattern sort, it might be exhausting to phase utilizing automated strategies, which means you should do it manually. If you happen to’ve generated a whole lot of knowledge, this might take years!
Nonetheless, most initiatives received’t be at this excessive fringe of issues, and weeks to months might be a extra affordable estimate.
And keep in mind, vEM know-how is in its infancy. Technological progress, pushed by bold analysis and data-sharing initiatives, will probably cut back these time frames to one thing extra possible.
The Present Challenges of vEM
So why isn’t everyone doing it? vEM and the group surrounding it are comparatively new. A number of challenges stop the method from being mainstream (for now).
Other than pattern preparation, which is user-dependent, among the challenges are as follows.
Information Assortment Time
vEM initiatives are intrinsically large-scale, and the information acquisition velocity of electron microscopes limits the quantity of information collected in a given interval. And unsurprisingly, there’s a trade-off between knowledge acquisition velocity and knowledge decision.
Inadequate {Hardware} Automation
And talking of large-scale initiatives, electron microscopes of any sort are sophisticated. Arrange and monitoring require devoted personnel, which means the common person can’t simply queue up a load of experiments and stroll away. The emergence of vEM might push electron microscope producers and amenities towards larger automation.
Dealing with Huge Portions of Information
Information dealing with and evaluation are additionally limiting steps as a result of vEM initiatives can generate terabytes of information. You possibly can’t simply slap it on a reminiscence stick and take it to the workplace. Such huge quantities of information are difficult to switch, not to mention analyze and interpret. And also you’ve received to again all of it up!
Information Segmentation
Imaging bigger areas has two main penalties: there’s extra knowledge to phase, and the information are extra biologically advanced. Think about segmenting all of the mitochondria in a cell—you get the concept. Fortuitously, machine- and deep-learning strategies are consistently evolving, which means that we’re all the time heading in the direction of extra correct, automated segmentation.
If you happen to genuinely should phase a whole lot of mitochondria, take a look at the AI device MitoNet. [3]
Inadequate Information Evaluation Automation and Streamlining
Equally, computerized picture annotation and segmentation strategies are nonetheless inadequate to annotate such wealthy and huge datasets precisely and reliably. Double-checking the outcomes of automated annotation additionally takes time. Assuredly knowledge evaluation and software program pipelines will develop tremendously.
3D Reconstruction is Onerous
Then there’s the apparent one—you should precisely align all the photographs to get a 3D reconstruction, which may be very exhausting. Take into account all of the picture artifacts and pattern distortions which will come up throughout knowledge acquisition, and it will get more durable nonetheless.
Into the Future: A Perspective on vEM
If these are challenges, what’s subsequent for vEM?
In a latest interview with us on The Microscopists, Lucy Collinson, Head of Electron Microscopy on the Francis Crick Institute, places the way forward for quantity electron microscopy like this:
The connectome map of the Caenorhabditis elegans worm’s mind exists because of vEM. [4] Now the trouble of the connectomics group is directed towards offering the connectome of the fly mind. As soon as they’ve managed this, they are going to most likely need to map the mouse connectome.
If the problem of mapping the C. elegans thoughts is equal to 1 airline seat, then the fly mind is the equal of 4 Boeing 747 jumbo jets, and the mouse mind is the equal of the gap between Boston, MA, and Lisbon.
Lucy has additionally co-authored a wonderful introduction to vEM [5] that goes into extra element than we do right here.
The challenges in pattern preparation, knowledge acquisition time, picture quantity, and knowledge evaluation are huge. Hopefully, the trouble expended in reaching them will usher within the subsequent technology of vEM know-how, making it extra accessible to each researcher.
References
- Motta A, Berning M, Boergens KM, et al. (2019) Dense connectomic reconstruction in layer 4 of the somatosensory cortex. Science 366:eaay3134
- Xu CS, Hayworth KJ, Lu Z, et al. (2017) Enhanced FIB-SEM programs for large-volume 3D imaging. Elife 6:e25916
- Glancy B (2023) MitoNet: A generalizable mannequin for segmentation of particular person mitochondria inside electron microscopy datasets. Cell Syst 14(1):7–8
- Mulcahy B, Witvliet D, Holmyard D, et al. (2018) A Pipeline for Quantity Electron Microscopy of the Caenorhabditis elegans Nervous System. Entrance Neural Circuits 12:94
- Collinson LM and Peddie CJ (2014) Exploring the third dimension: Quantity electron microscopy comes of age. Micron 61:9–19
[ad_2]