
[ad_1]
Core Ideas
An intramolecular pressure is a pressure that holds atoms collectively to kind a molecule. There are three predominant forms of these forces: covalent, ionic, and metallic, and every ends in completely different chemical properties. Intramolecular forces shouldn’t be confused with intermolecular forces, that are forces brought on by interactions between separate complete molecules.
Matters coated in different articles
What are Intramolecular Forces?
Intramolecular forces are the forces that maintain atoms collectively to kind molecules. There are a number of completely different ways in which atoms can work together with one another, which ends up in various kinds of forces between them. There are three predominant sorts, that are covalent, ionic, and metallic. Every pressure will maintain the molecule collectively in several methods, giving substances with numerous corresponding properties.
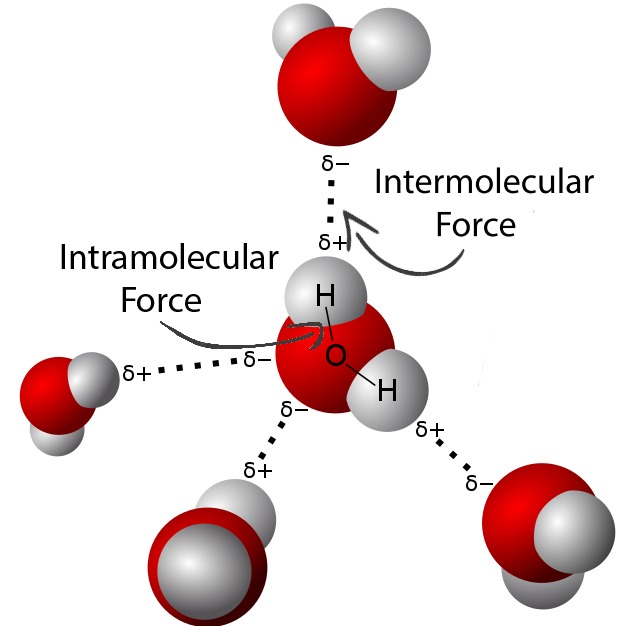
Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Forces
Regardless of being an analogous sounding phrase, intramolecular forces are completely different than intermolecular forces. Whereas intramolecular forces are between atoms inside a molecule, intermolecular forces are interactions between separate complete molecules, such because the hydrogen bonding that happens when a number of water molecules are close to one another. The numerous forms of intermolecular forces additionally create various properties in substances, however the kind of intermolecular pressure between molecules is closely influenced by the cost or polarity of a molecule, which comes from its intramolecular pressure. In distinction to the above instance, an intramolecular pressure in a water molecule can be the bond that retains the 2 H atoms connected to the O, and it’s due to the polarity of the covalent bond that hydrogen bonding happens the way in which it does, as proven under. For a extra in-depth analogy about how these forces are associated, see right here.
Forms of Intramolecular Forces
As beforehand acknowledged, there are a number of forms of intramolecular forces. Every sort creates various kinds of molecules, and subsequently completely different properties of the substances.
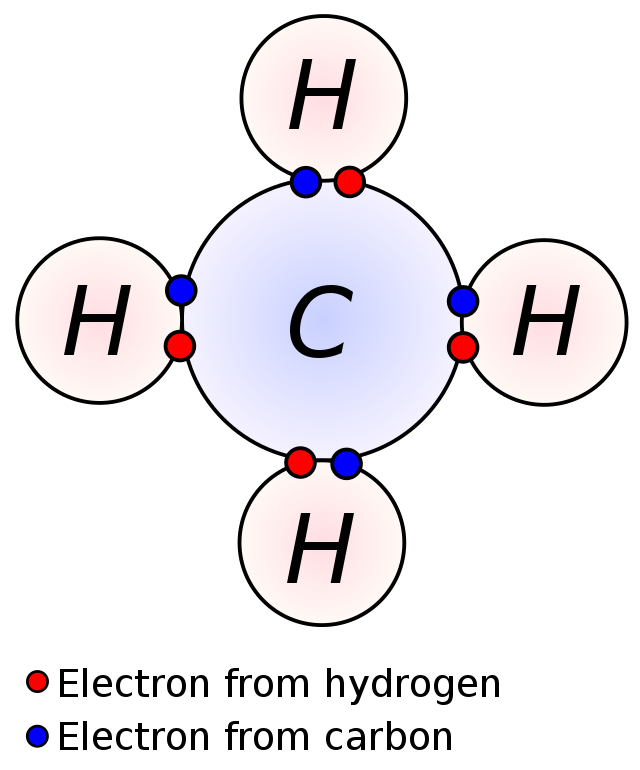
Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are the kind of pressure during which two atoms share an electron pair. These happen between two atoms which are looking for an octet (study extra about octets and the octet rule right here!), the place the atoms will concurrently maintain the identical electron pair of their respective valence shells, bonding them to one another. The diagram exhibits how two atoms share an electron pair, leading to a bond. This could occur to create both a polar bond or a nonpolar bond, relying on every atom’s electronegativity (affinity to tug electrons near them, study electronegativity in additional element right here).
Polar Covalent Bonds
When a covalent bond happens between two atoms with completely different electronegativities, the bond is polar. It is because one of many atoms may have a stronger affinity for the electrons than the opposite, and can pull them nearer to itself than the opposite atom. This creates a dipole, giving one atom a partial detrimental cost whereas the opposite has a partial optimistic cost. In some instances, dipoles might be so robust that they work together with surrounding ions or different polar molecules. These can be examples of intermolecular forces, which had been mentioned earlier.

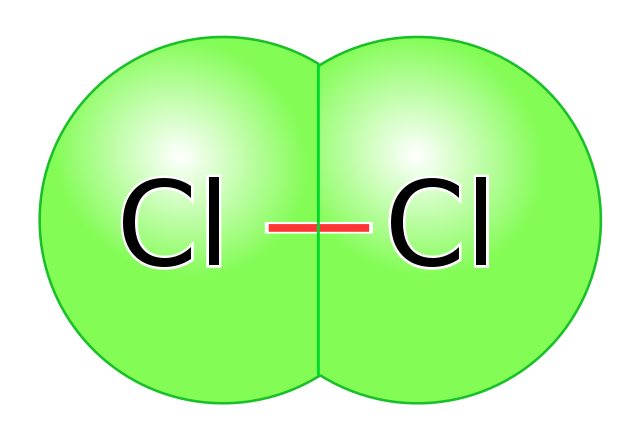
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Conversely, covalent bonds between atoms of the identical electronegativity produce nonpolar covalent bonds. A bond is nonpolar if neither atom pulls on the electrons stronger than the opposite, they usually find yourself completely shared between them. Oftentimes, this implies two of the identical atom covalently bonding to 1 one other the place the electronegativities are precisely equal, nevertheless there are additionally nonpolar covalent bonds between completely different atoms with extremely comparable electronegativities, akin to between carbon and hydrogen.
Ionic Bonds
In contrast to covalent bonds, ionic bonds don’t share electrons. As a substitute, an ionic bond happens when one atom donates an electron to a different one close by. This occurs when a steel and a nonmetal each search an octet. The steel will utterly switch certainly one of its valence electrons to the close by nonmetal, producing oppositely charged ions. These now steady ions then entice one another due to the opposing costs, creating an ionic pressure between them.

Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds are a bit completely different than the opposite two sorts. They solely happen inside metals, and since metals are likely to have a unfastened maintain on their electrons, the forces between steel atoms are distinctive. The nuclei of steel atoms stay in a single place, whereas all electrons can transfer across the nuclei, known as the “sea of electrons”. Due to this, metals are extremely conductive of electrical energy, since electrons and subsequently costs are simply capable of transfer round and be transferred all through it.

The intramolecular forces and interactions between molecules that create them are closely concerned with different subjects of chemistry. Which kind of intramolecular pressure a molecule has goes on to impact the way it interacts with different molecules round it, and thus the properties of any substance made up of it. Due to this, understanding intramolecular forces is vital to having a deeper understanding of what number of elements of chemistry works.
[ad_2]