[ad_1]
As our planet undergoes vital transformations as a result of local weather change, habitats are being altered, showing, disappearing, or altering in high quality. Understanding the influence of those modifications on the geographic distributions of species is of nice significance. The shrinking ranges of protected organisms and the increasing ranges of noxious species, akin to pests and pathogens, spotlight the pressing want to watch vary actions exactly.
Nevertheless, this process poses challenges because the obtainable commentary time is usually brief in comparison with the tempo of underlying inhabitants processes, making it tough to differentiate between directional shifts and random fluctuations.
Addressing this problem, a analysis crew led by Dr. Beáta Oborny from Loránd Eötvös College and the Centre for Ecological Analysis in Budapest has developed a novel methodology to watch vary shifts. The crew aimed to exactly and persistently delineate vary edges, permitting for comparisons between totally different years, geographic places, and species.
The paper is revealed within the journal Ecography.
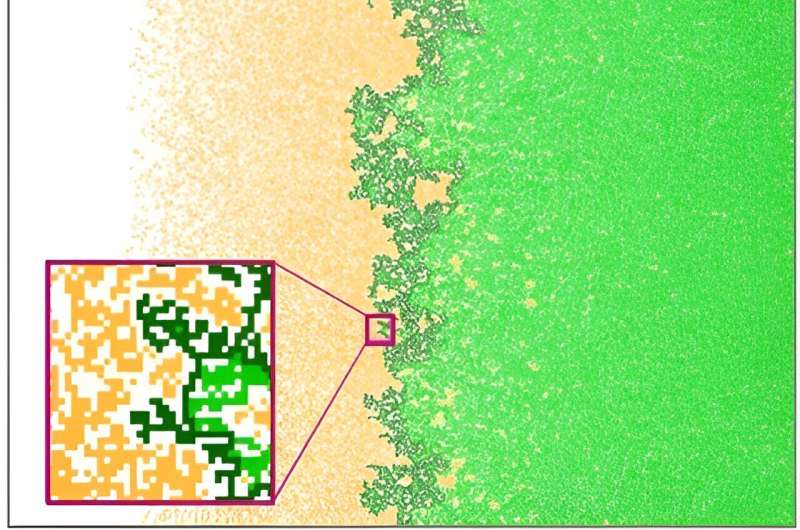
Delineating vary edges precisely is a non-trivial process as they usually exhibit complicated patterns. Occupied peninsulas are interspersed with unoccupied bays, and remoted occurrences dot the panorama. Whereas conventional strategies depend on the outermost occurrences of a species, Oborny and her colleagues suggest a special strategy.
They counsel marking the vary edge on the boundary between linked and fragmented occurrences, often called the “hull.” By marking the common place of the hull, the “connectivity restrict,” over time, the researchers supply a statistically extra dependable methodology. This area has the next inhabitants density and displays smaller fluctuations, enhancing the robustness of the strategy.
Oborny and her colleagues delved into the pattern-generating mechanisms utilizing spatially express fashions. Not like earlier approaches based mostly on normal spatial statistical strategies, their novel strategy capitalizes on information in regards to the mechanisms governing the emergence of those patterns: start, dispersal, and loss of life inside populations. By means of pc simulations alongside environmental gradients (e.g., hillsides), the crew explored the connectivity limits of various sorts of species.
Remarkably, they found that the hull displayed a sturdy fractal construction with a dimension of seven/4. Additional investigations performed by Beáta Oborny and Dániel Zimmermann confirmed that this fractal construction remained constant no matter whether or not the vary was quickly advancing or retreating in comparison with the era time. Notably, the tactic demonstrated explicit robustness within the retreating (trailing) fringe of species ranges.
These findings spotlight the applicability of the connectivity restrict in monitoring vary shifts throughout numerous geographic situations, enabling a world perspective on these modifications. For example, the tactic permits for the comparability of treelines in numerous mountains, even when composed of various species, using common scaling legal guidelines.
The common options uncovered on this research discover their rationalization in percolation principle, a discipline of analysis in statistical physics. This exemplifies the facility of information switch between seemingly disparate scientific disciplines.
The insights gained from these investigations deepen our understanding of the intricate relationship between environmental modifications and species distributions. As scientists proceed to refine and validate this methodology, it holds the potential to contribute to extra sturdy assessments of biodiversity shifts and inform efficient conservation methods.
Extra info:
Beáta Oborny et al, Advancing and retreating fronts in a altering local weather: a percolation mannequin of vary shifts, Ecography (2023). DOI: 10.1111/ecog.06645
Offered by
Institute of Aquatic Ecology, Centre for Ecological Analysis
Quotation:
Monitoring species vary shifts in a altering local weather (2023, August 21)
retrieved 21 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-tracking-species-range-shifts-climate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]