
[ad_1]
As an important a part of Carbon Seize, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) know-how, CO2 discount response (CO2RR) to carbon-based fuels and chemical substances presents broad utility prospects in renewable power storage and CO2 destructive emission.
Not too long ago, a group led by Prof. Tune Li and Affiliate Researcher He Qun from the Nationwide Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory of the College of Science and Expertise of China (USTC) of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS) put forth a novel understanding of the mechanism of CO2RR on the nickel (Ni) single-atomic websites. Their examine, titled “Uneven Dinitrogen-Coordinated Nickel Single-Atomic Websites for Environment friendly CO2 Electroreduction,” was revealed in Nature Communications.
A really perfect CO2RR catalyst requires low overpotential and excessive present density to merchandise. Nonetheless, former catalysts both are featured with excessive value and low present density, akin to gold (Au) and silver (Ag), often exhibit a lot larger overpotentials than Au and Ag, akin to Fe, Co, or Ni, limiting response effectivity.
Due to this fact, it’s crucial to develop overpotential low, excessive present density, plentiful 3d metal-based catalysts to switch treasured steel catalysts for CO2RR. To handle these challenges, the researchers proposed an uneven dinitrogen-coordinated nickel single-atom catalyst (Ni-N-C). By using the unsaturated and uneven traits of the websites, structural self-optimization throughout the electrochemical course of is achieved, thereby enhancing the intrinsic exercise of the websites in CO2RR.
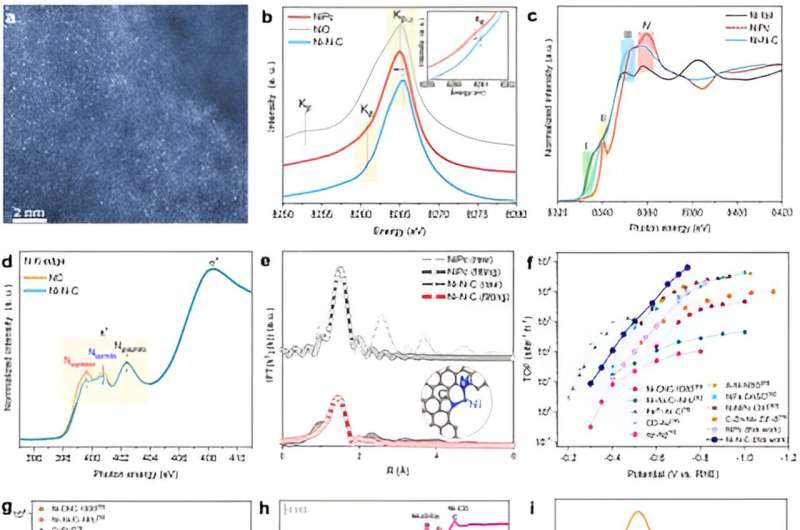
Within the examine, the group designed and synthesized Ni-N-C that includes dinitrogen coordination (pyridinic and pyrrolic nitrogen) after which utilized it for CO2 electroreduction reactions in impartial and alkaline media. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectra and emission spectra revealed the native coordination construction of Ni websites within the catalyst. The electrochemical check outcomes confirmed that the Ni-N-C catalyst may obtain very excessive electrochemical efficiency in each impartial (H-type cell) and alkaline (fuel diffusion electrode, GDE) electrolytes.
Particularly in alkaline circumstances, the catalyst may obtain a CO partial present density of 20.1 mA cmgeo-2 at -0.15 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (VRHE), Faraday effectivity of over 90% for CO within the potential vary of -0.15 to -0.9 VRHE, and excessive turnover frequency (TOF) of over 274,000 web site-1 h-1 at -1.0 VRHE, surpassing most reported catalysts.
This examine presents a novel comprehension of the catalyst‘s function within the CO2 electroreduction response and guarantees to shed new gentle on future CO2 discount applied sciences.
Extra data:
Yuzhu Zhou et al, Uneven dinitrogen-coordinated nickel single-atomic websites for environment friendly CO2 electroreduction, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39505-2
Offered by
College of Science and Expertise of China
Quotation:
Growing new catalysts for carbon dioxide electroreduction (2023, August 11)
retrieved 11 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-catalysts-carbon-dioxide-electroreduction.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]